Pedicled Chimeric Perforator Flap Based on Inferior Gluteal Vessel Axis for the Reconstruction of Stage-Four Primary Ischial Pressure Sores-A New Design
- PMID: 34239241
- PMCID: PMC8257320
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1729505
Pedicled Chimeric Perforator Flap Based on Inferior Gluteal Vessel Axis for the Reconstruction of Stage-Four Primary Ischial Pressure Sores-A New Design
Abstract
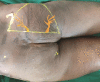
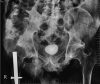
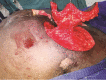
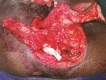
Background "Subfascial void reconstruction" in ischial pressure sores (IPSs) goes a long way in the amelioration of the common complications like persistent drainage, infection, wound dehiscence, and late recurrence. No locoregional flaps suffice this requirement. So we have designed a chimeric pedicled flap based on the inferior gluteal vessel axis (IGVA) perforators with two tissue components: (1) Pacman-style fasciocutaneous flap on a perforator and (2) gluteus maximus muscle (inferior portion) on another independent perforator. Aim and Methods After confirming the feasibility of novel design of chimeric pedicled IGVA perforator flap with cadaver study, we embarked on the clinical study with this chimeric flap. In this prospective cohort study, the study and the control existed in the same patient so that the biological factors affecting the wound healing would be the same. Results Twenty-one patients were included whose mean age was 39 years. Late recurrence occurred in one patient (4.8%) of chimeric flap while the control group (who had undergone conventional reconstruction) had recurrence in 11 patients (52.4%). On assessment with overall institutional score, grade A was observed in 18 patients of the chimeric IGVA flap group ( p < 0.045), and in only 3 patients of the control group. Conclusions This anatomically construed flap, a new addendum in the armamentarium of reconstruction of IPSs, with its potential to congruently fill the ischiogluteal subfascial void may provide a lasting solution for preventing recurrences.
Keywords: chimeric inferior gluteal artery perforator flap; ischial pressure ulcer; myelopathic patients; recurrent pressure ulcer.
Association of Plastic Surgeons of India. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestFinancial Support and Sponsorship None declared. None.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Successful reconstruction of ischial pressure sores with inferior gluteal artery descending branch perforator flap.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):3692-3698. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1619. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33752419
-
A dual padding method for ischial pressure sore reconstruction with an inferior gluteal artery perforator fasciocutaneous flap and a split inferior gluteus maximus muscle flap.Arch Plast Surg. 2019 Sep;46(5):455-461. doi: 10.5999/aps.2019.00031. Epub 2019 Sep 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31550751 Free PMC article.
-
[The infragluteal perforator flap].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2006 Dec;38(6):390-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-924741. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2006. PMID: 17219322 German.
-
The pedicled internal pudendal artery perforator (PIPAP) flap for ischial pressure sore reconstruction: Technique and long-term outcome of a cohort study.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 Jun;71(6):889-894. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.01.032. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 29428586
-
[Defect coverage using gluteal flaps].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2018 Aug;30(4):236-244. doi: 10.1007/s00064-018-0549-5. Epub 2018 May 9. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2018. PMID: 29744524 Review. German.
Cited by
-
[Clinical effects of island posterior femoral composite tissue flaps in the repair of sinus cavity pressure ulcers in the areas of ischial tuberosity and greater trochanter].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023 Jan 20;39(1):65-70. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20220420-00148. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36740428 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Can surface landmarks help us identify the gibson interval during surgical hip dislocation: a study of 617 hips.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Dec 18;145(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05622-w. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39694892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel and Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance In: Haesler E, ed. Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: Quick Reference Guide. Osborne Park, Australia: Cambridge Media2014
-
- Dansereau J G, Conway H. Closure of decubiti in paraplegic. Report of 2000 Cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1964;33:474–480. - PubMed
-
- Kwon R, Janis J E. Pressure sores. In: Neligan PC, ed. Plastic Surgery. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. 2018:351–382.
-
- Chen Y, Devivo M J, Jackson A B. Pressure ulcer prevalence in people with spinal cord injury: age-period-duration effects. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(06):1208–1213. - PubMed
-
- Cushing C A, Phillips L G. Evidence-based medicine: pressure sores. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132(06):1720–1732. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

