Hepatitis delta virus: From infection to new therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 34239267
- PMCID: PMC8240063
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3530
Hepatitis delta virus: From infection to new therapeutic strategies
Abstract
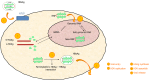
The hepatitis delta virus (HDV) is a small RNA virus that encodes a single protein and which requires the hepatitis B virus (HBV)-encoded hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for its assembly and transmission. HBV/HDV co-infections exist worldwide and show a higher prevalence among selected groups of HBV-infected populations, specifically intravenous drug users, practitioners of high-risk sexual behaviours, and patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The chronic form of HDV-related hepatitis is usually severe and rapidly progressive. Patterns of the viral infection itself, including the status of co-infection or super-infection, virus genotypes (both for HBV and HDV), and persistence of the virus' replication, influence the outcome of the accompanying and manifested liver disease. Unfortunately, disease severity is burdened by the lack of an effective cure for either virus type. For decades, the main treatment option has been interferon, administered as mono-therapy or in combination with nucleos(t)ide analogues. While its efficacy has been reported for different doses, durations and courses, only a minority of patients achieve a sustained response, which is the foundation of eventual improvement in related liver fibrosis. The need for an efficient therapeutic alternative remains. Research efforts towards this end have led to new treatment options that target specific steps in the HDV life cycle; the most promising among these are myrcludex B, which inhibits virus entry into hepatocytes, lonafarnib, which inhibits farnesylation of the viral-encoded L-HDAg large hepatitis D antigen, and REP-2139, which interferes with HBsAg release and assembly.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; Hepatitis delta virus; Lonafarnib; Myrcludex; REP 2139.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rizzetto M. The adventure of delta. Liver Int. 2016;36 Suppl 1:135–140. - PubMed
-
- Sureau C, Negro F. The hepatitis delta virus: Replication and pathogenesis. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S102–S116. - PubMed
-
- Chen HY, Shen DT, Ji DZ, Han PC, Zhang WM, Ma JF, Chen WS, Goyal H, Pan S, Xu HG. Prevalence and burden of hepatitis D virus infection in the global population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 2019;68:512–521. - PubMed

