Superhydrophobic Surface for Enhancing the Bioavailability of Salbutamol Sulfate from Cross-Linked Microspheres: Formulation, Characterization, and in vivo Evaluation
- PMID: 34239296
- PMCID: PMC8259835
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S309078
Superhydrophobic Surface for Enhancing the Bioavailability of Salbutamol Sulfate from Cross-Linked Microspheres: Formulation, Characterization, and in vivo Evaluation
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the work was to formulate salbutamol sulfate (SB) microspheres by using superhydrophobic surface (SHS) under different processing factors for improving its encapsulation efficiency, controling its release rate, and hence enhancing its bioavailability.
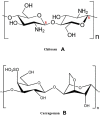
Methods: Cross-linked microspheres of chitosan (CN) and carrageenan (KN) were made on a SHS under a glutaraldehyde-saturated atmosphere. The formulations were designed and optimized based on 42 factorial design. Percentage encapsulation efficiency (%EE), particle size, swelling ratio, and in vitro release rate were characterized, and the in vivo performance of optimized formula was investigated in beagle dogs.
Results: The results showed that the prepared microspheres have a high %EE (97.11±0.78%) for F13. The swelling ratio was 4.2 at the end of the 8 hours for the optimized formula, and the in vitro release rate was controlled for 12 hours. In vivo study verified that there was a 1.61-fold enhancement in SB bioavailability from optimized formula (F13) compared to market tablet.
Conclusion: The study suggested that microspheres prepared from CN/KN crosslinking on an SHS using glutaraldehyde atmosphere is a promising technique that can encapsulate and sustain the release of water-soluble drugs such as SB in addition to improving its in vivo pharmacokinetic profile.
Keywords: bioavailability; cross-linked complex; microspheres; salbutamol sulfate; superhydrophobic; sustain release; water-soluble drugs.
© 2021 Gaber et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Controlled release chitosan microspheres of mirtazapine: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Nov;34(11):1919-29. doi: 10.1007/s12272-011-1112-1. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Arch Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 22139691
-
Dual cross-linked chitosan microspheres formulated with spray-drying technique for the sustained release of levofloxacin.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Apr;45(4):568-576. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1569025. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30652515
-
Chemical cross-linking: A feasible approach to prolong doxylamine/pyridoxine release from spray-dried chitosan microspheres.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Oct 15;123:387-394. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.07.059. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30077710
-
[Preparation of uniform-sized chitosan microspheres and application as carriers for protein drugs].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;22(1):150-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16572856 Chinese.
-
Superhydrophobic Surface-Assisted Preparation of Microspheres and Supraparticles and Their Applications.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):68. doi: 10.1007/s40820-023-01284-2. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 38175452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development, in vitro Evaluation, and in vivo Study of Adhesive Buccal Films for the Treatment of Diabetic Pediatrics via Trans Mucosal Delivery of Gliclazide.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Dec 13;16:4235-4250. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S394523. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36536629 Free PMC article.
-
Application of nano- and micro-particle-based approaches for selected bronchodilators in management of asthma.3 Biotech. 2024 Sep;14(9):208. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04051-1. Epub 2024 Aug 23. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39184911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nardi-Ricart A, Nofrerias-Roig I, Suñé-Pou M, et al. Formulation of sustained release hydrophilic matrix tablets of tolcapone with the application of sedem diagram: influence of tolcapone’s particle size on sustained release. Pharmaceutics. 2020;17(12):674–688. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12070674 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moustafine RI, Margulis EB, Sibgatullina LF, Kemenova VA, Mooter GVD. Comparative evaluation of interpolyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan with eudragit® L100 and eudragit® L100-55 as potential carriers for oral controlled drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;70:215–225. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.04.008 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

