CircHIPK3 regulates pulmonary fibrosis by facilitating glycolysis in miR-30a-3p/FOXK2-dependent manner
- PMID: 34239356
- PMCID: PMC8241722
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.57915
CircHIPK3 regulates pulmonary fibrosis by facilitating glycolysis in miR-30a-3p/FOXK2-dependent manner
Abstract
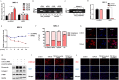
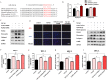
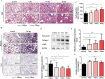
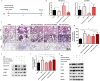
Pulmonary fibrosis develops when myofibroblasts and extracellular matrix excessively accumulate in the injured lung, but what drives fibrosis is not fully understood. Glycolysis has been linked to cell growth and proliferation, and several studies have shown enhanced glycolysis promotes pulmonary fibrosis. However, detailed studies describing this switch remain limited. Here, we identified that TGF-β1 effectively increased the expression of circHIPK3 in lung fibroblasts, and circHIPK3 inhibition attenuated the activation, proliferation, and glycolysis of fibroblasts in vitro. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assays, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), and RNA pull-down assays showed that circHIPK3 could function as a sponge of miR-30a-3p and inhibit its expression. Furthermore, FOXK2, a driver transcription factor of glycolysis, was identified to be a direct target of miR-30a-3p. Mechanistically, circHIPK3 could enhance the expression of FOXK2 via sponging miR-30a-3p, thereby facilitating fibroblast glycolysis and activation. Besides, miR-30a-3p overexpression or FOXK2 knockdown blocked fibroblast activation induced by TGF-β1 and abrogated the profibrotic effects of circHIPK3. Moreover, circHIPK3 and miR-30a-3p were also dysregulated in fibrotic murine lung tissues induced by silica. Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated circHIPK3 silence or miR-30a-3p overexpression alleviated silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in vivo. In conclusion, our results identified circHIPK3/miR-30a-3p/FOXK2 regulatory pathway as an important glycolysis cascade in pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: FOXK2; ceRNA; circHIPK3; glycolysis; silicosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Green FH. Overview of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2002;122:334s–9s. - PubMed
-
- Leung CC, Yu IT, Chen W. Silicosis. Lancet (London, England) 2012;379:2008–18. - PubMed
-
- Wuyts WA, Agostini C, Antoniou KM, Bouros D, Chambers RC, Cottin V. et al. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: a moving target. The European respiratory journal. 2013;41:1207–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

