Strenuous Physical Training, Physical Fitness, Body Composition and Bacteroides to Prevotella Ratio in the Gut of Elderly Athletes
- PMID: 34239449
- PMCID: PMC8257935
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.670989
Strenuous Physical Training, Physical Fitness, Body Composition and Bacteroides to Prevotella Ratio in the Gut of Elderly Athletes
Abstract
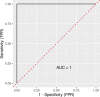
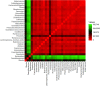
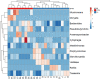
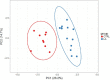
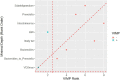
Regular physical activity seems to have a positive effect on the microbiota composition of the elderly, but little is known about the added possible benefits of strenuous endurance training. To gain insight into the physiology of the elderly and to identify biomarkers associated with endurance training, we combined different omics approaches. We aimed to investigate the gut microbiome, plasma composition, body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, and muscle strength of lifetime elderly endurance athletes (LA) age 63.5 (95% CI 61.4, 65.7), height 177.2 (95% CI 174.4, 180.1) cm, weight 77.8 (95% CI 75.1, 80.5) kg, VO2max 42.4 (95% CI 39.8, 45.0) ml.kg-1.min-1 (n = 13) and healthy controls age 64.9 (95% CI 62.1, 67.7), height 174.9 (95% CI 171.2, 178.6) cm, weight 83.4 (95% CI 77.1, 89.7) kg, VO2max 28.9 (95% CI 23.9, 33.9), ml.kg-1.min-1 (n = 9). Microbiome analysis was performed on collected stool samples further subjected to 16S rRNA gene analysis. NMR-spectroscopic analysis was applied to determine and compare selected blood plasma metabolites mostly linked to energy metabolism. The machine learning (ML) analysis discriminated subjects from the LA and CTRL groups using the joint predictors Bacteroides 1.8E + 00 (95% CI 1.1, 2.5)%, 3.8E + 00 (95% CI 2.7, 4.8)% (p = 0.002); Prevotella 1.3 (95% CI 0.28, 2.4)%, 0.1 (95% CI 0.07, 0.3)% (p = 0.02); Intestinimonas 1.3E-02 (95% CI 9.3E-03, 1.7E-02)%, 5.9E-03 (95% CI 3.9E-03, 7.9E-03)% (p = 0.002), Subdoligranulum 7.9E-02 (95% CI 2.5E-02, 1.3E-02)%, 3.2E-02 (95% CI 1.8E-02, 4.6E-02)% (p = 0.02); and the ratio of Bacteroides to Prevotella 133 (95% CI -86.2, 352), 732 (95% CI 385, 1079.3) (p = 0.03), leading to an ROC curve with AUC of 0.94. Further, random forest ML analysis identified VO2max, BMI, and the Bacteroides to Prevotella ratio as appropriate, joint predictors for discriminating between subjects from the LA and CTRL groups. Although lifelong endurance training does not bring any significant benefit regarding overall gut microbiota diversity, strenuous athletic training is associated with higher cardiorespiratory fitness, lower body fat, and some favorable gut microbiota composition, all factors associated with slowing the rate of biological aging.
Keywords: VO2max; aging; body fat; exercise; microbiome.
Copyright © 2021 Šoltys, Lendvorský, Hric, Baranovičová, Penesová, Mikula, Bohmer, Budiš, Vávrová, Grones, Grendar, Kolísek and Bielik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) (2013). ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
-
- Andrews S. (2018). FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online at: https://github.com/s-andrews/FastQC (accessed January 15, 2021).
-
- Barton W., Penney N. C., Cronin O., Garcia-Perez I., Molloy M. G., Holmes E., et al. (2017). The microbiomes of professional athletes differ from those of more sedentary subjects in composition and particularly at the functional metabolic level. Gut 67 625–633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

