Vagus Nerve Cross-Sectional Area in Patients With Parkinson's Disease-An Ultrasound Case-Control Study
- PMID: 34239497
- PMCID: PMC8258145
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.681413
Vagus Nerve Cross-Sectional Area in Patients With Parkinson's Disease-An Ultrasound Case-Control Study
Abstract
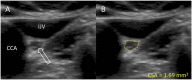
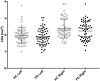
Background: Vagal parasympathetic neurons are prone to degeneration in Parkinson's disease (PD). High-resolution ultrasound can precisely estimate the cross-sectional (CSA) area of peripheral nerves. Here, we tested the hypothesis that vagus CSA is reduced in PD. Methods: We included 56 healthy controls (HCs) and 63 patients with PD. Using a high-end ultrasound system equipped with a high-frequency transducer, five images were obtained of each nerve. The hypoechoic neuronal tissue was delineated offline with dedicated software and the CSA extracted. Results: In the initial PD vs. HC comparison, no statistically significant differences were observed in mean left vagus CSA (HC: 1.97 mm2, PD: 1.89 mm2, P = 0.36) nor in mean right vagus CSA (HC: 2.37 mm2, PD: 2.23 mm2, P = 0.17). The right vagus CSA was significantly larger than the left vagus CSA in both groups (P < 0.0001). Females were overrepresented in the HC group and presented with generally smaller vagus CSAs. Consequently, sex-adjusted CSA was significantly smaller for the right vagus nerve of the PD group (P = 0.041), but not for the left. Conclusion: A small but significant reduction in sex-adjusted right vagus CSA was observed in patients with PD. The left vagus CSA was not significantly reduced in patients with PD. Ultrasound may not be a suitable method to detecting vagal axonal loss in individual patients.
Keywords: cross-sectional area; parasympathetic; parkinson's disease; ultrasound; vagus nerve.
Copyright © 2021 Horsager, Walter, Fedorova, Andersen, Skjærbæk, Knudsen, Okkels, von Weitzel-Mudersbach, Dyrskog, Bergholt and Borghammer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cross-sectional area of the vagus nerve is not reduced in Parkinson's disease patients.eNeurologicalSci. 2022 May 5;27:100400. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2022.100400. eCollection 2022 Jun. eNeurologicalSci. 2022. PMID: 35592106 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal Degeneration of the Vagus Nerve in Parkinson's Disease-A High-Resolution Ultrasound Study.Front Neurol. 2018 Nov 12;9:951. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00951. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30483212 Free PMC article.
-
Vagal cross-sectional area correlates with parasympathetic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease.Brain Commun. 2023 Jan 18;5(1):fcad006. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad006. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 36726777 Free PMC article.
-
Vagus nerve ultrasonography in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Auton Neurosci. 2021 Sep;234:102835. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2021.102835. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Auton Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34166995
-
Ultrasonographically measured atrophy of vagus nerve in Parkinson's Disease: clinical and pathogenetic insights plus systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2024;58(5):471-483. doi: 10.5603/pjnns.99592. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2024. PMID: 39140586
Cited by
-
Comparison of vagus nerve cross-sectional area between brain-first and body-first Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Dec 5;10(1):231. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00844-6. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39639003 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-sectional area of the vagus nerve is not reduced in Parkinson's disease patients.eNeurologicalSci. 2022 May 5;27:100400. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2022.100400. eCollection 2022 Jun. eNeurologicalSci. 2022. PMID: 35592106 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound evaluation of vagus nerve cross-sectional area in a community-dwelling elderly Japanese cohort.PLoS One. 2023 May 18;18(5):e0280661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280661. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37200343 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Visualization of Pig Vagus Nerve "Vagotopy" Using Ultrasound.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 25;15:676680. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.676680. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899151 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Parkinson's Disease on Cardio-postural Coupling During Orthostatic Challenge.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 3;13:863877. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.863877. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35755448 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

