Immunomodulation and Intestinal Morpho-Functional Aspects of a Novel Gram-Negative Bacterium Rouxiella badensis subsp. acadiensis
- PMID: 34239502
- PMCID: PMC8258396
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.569119
Immunomodulation and Intestinal Morpho-Functional Aspects of a Novel Gram-Negative Bacterium Rouxiella badensis subsp. acadiensis
Abstract
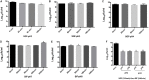
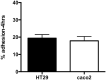
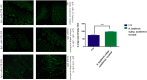
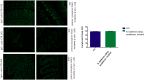
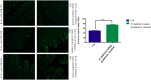
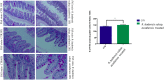
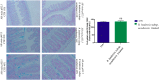
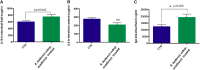
A novel bacterium (Rouxiella badensis subsp. acadiensis) isolated from the microbiota of wild blueberry fruit was investigated for its immunomodulation capabilities and intestinal morpho-functional aspects. The whole-genome shotgun sequencing of this bacterium led to its new taxonomy and showed absence of pathogenicity genes. Although the bacterium was used for blueberry-fermentation and enhancing its anti-inflammatory effects on neurodegeneration, diabetes, and cancer, no study has assessed the effect of the bacterium on health. In this study, we used several in vitro and in vivo assays to evaluate the interaction of R. badensis subsp. acadiensis with the intestinal mucosa and its impact on the localized immune response. The strain antibiotic susceptibility has been investigated as well as its tolerance to gastric and intestinal environment and ability to attach to human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2 and HT-29). In addition, Balb/c mice were used to explore the immune-modulatory characteristics of the live bacterium at the intestinal level and its impact on the morpho-functional aspects of the intestinal mucosa. In vitro assays revealed the ability of R. badensis subsp. acadiensis to survive the gastric and intestinal simulated conditions and to satisfactorily adhere to the human intestinal epithelial cells. The bacterium was shown to be sensitive to an array of antibiotics. Immuno-modulation studies with mice orally administered with R. badensis subsp. acadiensis showed a higher number of IgA positive cells in the small intestine, a higher concentration of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in the intestinal mucosa, as well as an increase in the number of goblet cells. The anti-inflammatory cytokine miR146a was found to be increased in the ileum and brain. Furthermore, it increases the number of goblet cells which contribute to intestinal barrier integrity. Taken together, our findings reflect the ability of the tested bacterium to modulates the intestinal homeostasis and immune response. Detailed safety unpublished studies and genome data support our finding. The strain Rouxiella badensis subsp. acadiensis has been filed in a provisional patent; a U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/916,921 entitled "Probiotics Composition and Methods." Future studies are still needed to validate the potential utilization of this strain as functional food and its potential probiotic effect.
Keywords: gastro-intestinal tolerance; immuno-modulation; micoRNAs (miRNAs); mucosal immunity; probiotic.
Copyright © 2021 Yahfoufi, Alsadi, Mallet, Kulshreshtha, Hincke, Ismail and Matar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alderberth I., Cerquetti M., Poilance I., Wold A., Collignon A. (2000). Mechanisms of Colonisation and Colonisation Resistance of the Digestive Tract. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 12 223–239. 10.3402/mehd.v12i2.8060 - DOI
-
- Arboleya S., Ruas-Madiedo P., Margolles A., Solís G., Salminen S., de los Reyes-Gavilán C. G., et al. (2011). Characterization and in Vitro Properties of Potentially Probiotic Bifidobacterium Strains Isolated from Breast-Milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 149 28–36. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.10.036 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

