Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Have Lower Levels of Antibody to Heat-Stressed Fibroblast Derived Proteins, versus Normal Subjects
- PMID: 34239605
- PMCID: PMC8225444
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5577218
Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Have Lower Levels of Antibody to Heat-Stressed Fibroblast Derived Proteins, versus Normal Subjects
Abstract
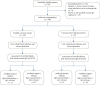
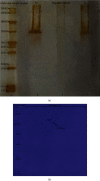
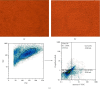
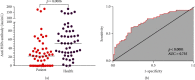
Cellular stress response plays an important role in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease (CAD). Inhibition of cellular stress may provide a novel clinical approach regarding the diagnosis and treatment of CAD. Fibroblasts constitute 60-70% of cardiac cells and have a crucial role in cardiovascular function. Hence, the aim of this study was to show a potential therapeutic application of proteins derived from heat-stressed fibroblast in CAD patients. Fibroblasts were isolated from the foreskin and cultured under heat stress conditions. Surprisingly, 1.06% of the cells exhibited a necrotic death pattern. Furthermore, heat-stressed fibroblasts produced higher level of total proteins than control cells. In SDS-PAGE analysis, a 70 kDa protein band was observed in stressed cell culture supernatants which appeared as two acidic spots with close pI in the two-dimensional electrophoresis. To evaluate the immunogenic properties of fibroblast-derived heat shock proteins (HSPs), the serum immunoglobulin-G (IgG) was measured by ELISA in 50 CAD patients and 50 normal subjects who had been diagnosed through angiography. Interestingly, the level of anti-HSP antibody was significantly higher in non-CAD individuals in comparison with the patient's group (p < 0.05). The odds ratio for CAD was 5.06 (95%CI = 2.15-11.91) in cut-off value of 30 AU/mL of anti-HSP antibody. Moreover, ROC analysis showed that anti-HSP antibodies had a specificity of 74% and a sensitivity of 64%, which is almost equal to 66% sensitivity of exercise stress test (EST) as a CAD diagnostic method. These data revealed that fibroblast-derived HSPs are suitable for the diagnosis and management of CAD through antibody production.
Copyright © 2021 Azin Aghamajidi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there is no conflict of interest in publication of this contribution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum antibody titers against heat shock protein 27 are associated with the severity of coronary artery disease.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 May;16(3):309-16. doi: 10.1007/s12192-010-0241-7. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011. PMID: 21107776 Free PMC article.
-
Serum immunoglobulin G antibodies to chlamydial heat shock protein 60 but not to human and bacterial homologs are associated with coronary artery disease.Circulation. 2002 Sep 24;106(13):1659-63. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000031567.10814.d8. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 12270859
-
Antibodies against the human heat shock protein hsp70 in patients with severe coronary artery disease.Immunol Invest. 2002 Aug-Nov;31(3-4):219-31. doi: 10.1081/imm-120016242. Immunol Invest. 2002. PMID: 12472181
-
Molecular mimicry in atherosclerosis: a role for heat shock proteins in immunisation.Atherosclerosis. 2003 Apr;167(2):177-85. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(02)00301-5. Atherosclerosis. 2003. PMID: 12818399 Review.
-
[Heat shock proteins and their characteristics].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005 Aug;19(110):215-9. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005. PMID: 16245438 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Proteome analysis, bioinformatic prediction and experimental evidence revealed immune response down-regulation function for serum-starved human fibroblasts.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 22;9(9):e19238. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19238. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37674821 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

