Temporal change in inflammatory biomarkers and risk of cardiovascular events: the Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34240828
- PMCID: PMC8497383
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13445
Temporal change in inflammatory biomarkers and risk of cardiovascular events: the Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Aims: Little is known about the association of temporal changes in inflammatory biomarkers and the risk of death and cardiovascular diseases. We aimed to evaluate the association between temporal changes in C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and risk of heart failure (HF), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and all-cause mortality in individuals without a history of prior CVD.
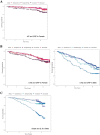
Methods and results: Participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) cohort with repeated measures of inflammatory biomarkers and no CVD event prior to the second measure were included. Quantitative measures, annual change, and biomarker change categories were used as main predictors in Cox proportional hazard models stratified based on sex and statin use. A total of 2258 subjects (50.6% female, mean age of 62 years) were studied over an average of 8.1 years of follow-up. The median annual decrease in CRP levels was 0.08 mg/L. Fibrinogen and IL-6 levels increased by a median of 30 mg/dL and 0.24 pg/mL annually. Temporal changes in CRP were positively associated with HF risk among females (HR: 1.18 per each standard deviation increase, P < 0.001) and other CVD in both female (HR: 1.12, P = 0.004) and male participants (HR: 1.24, P = 0.003). The association of CRP change with HF and other CVD was consistently observed in statin users (HR: 1.23 per SD increase, P = 0.001 for HF and HR: 1.19 per SD increase, P < 0.001 for other CVD). There were no significant associations between temporal changes of fibrinogen or IL-6 with HF or other CVD. Men with sustained high values of IL-6 had a 2.3-fold higher risk of all-cause mortality (P < 0.001) compared with those with sustained low values.
Conclusions: Temporal change in CRP is associated with HF only in women and statin users, and other CVD in both women and men, and statin users. Annual changes in fibrinogen and IL-6 were not predictive of cardiovascular outcomes in either sex.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Fibrinogen; Heart failure; Interleukin; Longitudinal cohort study.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors of this work has nothing to disclose. All authors declare that the submitted work is original and has not been published and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. The views expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institutes of Health; or the US Department of Health and Human Services.
Figures

References
-
- Pearson TA, Mensah GA, Alexander RW, Anderson JL, Cannon RO 3rd, Criqui M, Fadl YY, Fortmann SP, Hong Y, Myers GL, Rifai N, Smith SC Jr, Taubert K, Tracy RP, Vinicor F. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: application to clinical and public health practice: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2003; 107: 499–511. - PubMed
-
- Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Pennells L, Wood AM, White IR, Gao P, Walker M, Thompson A, Sarwar N, Caslake M, Butterworth AS, Amouyel P, Assmann G, Bakker SJ, Barr EL, Barrett‐Connor E, Benjamin EJ, Björkelund C, Brenner H, Brunner E, Clarke R, Cooper JA, Cremer P, Cushman M, Dagenais GR, D'Agostino RB, Sr Dankner R, Davey‐Smith G, Deeg D, Dekker JM, Engström G, Folsom AR, Fowkes FG, Gallacher J, Gaziano JM, Giampaoli S, Gillum RF, Hofman A, Howard BV, Ingelsson E, Iso H, Jørgensen T, Kiechl S, Kitamura A, Kiyohara Y, Koenig W, Kromhout D, Kuller LH, Lawlor DA, Meade TW, Nissinen A, Nordestgaard BG, Onat A, Panagiotakos DB, Psaty BM, Rodriguez B, Rosengren A, Salomaa V, Kauhanen J, Salonen JT, Shaffer JA, Shea S, Ford I, Stehouwer CD, Strandberg TE, Tipping RW, Tosetto A, Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Wennberg P, Westendorp RG, Whincup PH, Wilhelmsen L, Woodward M, Lowe GD, Wareham NJ, Khaw KT, Sattar N, Packard CJ, Gudnason V, Ridker PM, Pepys MB, Thompson SG, Danesh J. C‐reactive protein, fibrinogen, and cardiovascular disease prediction. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1310–1320. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo JP, Lourenco P, Azevedo A, Frioes F, Rocha‐Goncalves F, Ferreira A, Bettencourt P. Prognostic value of high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein in heart failure: a systematic review. J Card Fail 2009; 15: 256–266. - PubMed
-
- Bahrami H, Bluemke DA, Kronmal R, Bertoni AG, Lloyd‐Jones DM, Shahar E, Szklo M, Lima JA. Novel metabolic risk factors for incident heart failure and their relationship with obesity: the MESA (Multi‐Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008; 51: 1775–1783. - PubMed
-
- Cainzos‐Achirica M, Miedema MD, McEvoy JW, Cushman M, Dardari Z, Greenland P, Nasir K, Budoff MJ, Al‐Mallah MH, Yeboah J, Blumenthal RS, Comin‐Colet J, Blaha MJ. The prognostic value of high sensitivity C‐reactive protein in a multi‐ethnic population after >10 years of follow‐up: the Multi‐Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Int J Cardiol 2018; 264: 158–164. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01HC95168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111362/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

