Dissection of pleiotropic effects of variants in and adjacent to F8 exon 19 and rescue of mRNA splicing and protein function
- PMID: 34242570
- PMCID: PMC8387460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.06.012
Dissection of pleiotropic effects of variants in and adjacent to F8 exon 19 and rescue of mRNA splicing and protein function
Abstract
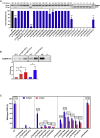
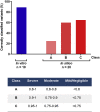
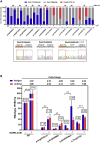
The pathogenic significance of nucleotide variants commonly relies on nucleotide position within the gene, with exonic changes generally attributed to quantitative or qualitative alteration of protein biosynthesis, secretion, activity, or clearance. However, these changes may exert pleiotropic effects on both protein biology and mRNA splicing due to the overlapping of the amino acid and splicing codes, thus shaping the disease phenotypes. Here, we focused on hemophilia A, in which the definition of F8 variants' causative role and association to bleeding phenotypes is crucial for proper classification, genetic counseling, and management of affected individuals. We extensively characterized a large panel of hemophilia A-causing variants (n = 30) within F8 exon 19 by combining and comparing in silico and recombinant expression analyses. We identified exonic variants with pleiotropic effects and dissected the altered protein features of all missense changes. Importantly, results from multiple prediction algorithms provided qualitative results, while recombinant assays allowed us to correctly infer the likely phenotype severity for 90% of variants. Molecular characterization of pathogenic variants was also instrumental for the development of tailored correction approaches to rescue splicing affecting variants or missense changes impairing protein folding. A single engineered U1snRNA rescued mRNA splicing of nine different variants and the use of a chaperone-like drug resulted in improved factor VIII protein secretion for four missense variants. Overall, dissection of the molecular mechanisms of a large panel of HA variants allowed precise classification of HA-affected individuals and favored the development of personalized therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: F8; FVIII; RNA; bioinformatic; haemophilia; hemophilia; missense; pleiotropic effect; prediction; splicing.
Copyright © 2021 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.P. is the inventor of a patent (PCT/IB2011/054573) on modified U1snRNAs. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Peyvandi F., Garagiola I., Young G. The past and future of haemophilia: diagnosis, treatments, and its complications. Lancet. 2016;388:187–197. - PubMed
-
- McVey J.H., Rallapalli P.M., Kemball-Cook G., Hampshire D.J., Giansily-Blaizot M., Gomez K., Perkins S.J., Ludlam C.A. The European Association for Haemophilia and Allied Disorders (EAHAD) Coagulation Factor Variant Databases: Important resources for haemostasis clinicians and researchers. Haemophilia. 2020;26:306–313. - PubMed
-
- Lakich D., Kazazian H.H., Jr., Antonarakis S.E., Gitschier J. Inversions disrupting the factor VIII gene are a common cause of severe haemophilia A. Nat. Genet. 1993;5:236–241. - PubMed
-
- Bagnall R.D., Waseem N., Green P.M., Giannelli F. Recurrent inversion breaking intron 1 of the factor VIII gene is a frequent cause of severe hemophilia A. Blood. 2002;99:168–174. - PubMed
-
- Jourdy Y., Nougier C., Roualdes O., Fretigny M., Durand B., Negrier C., Vinciguerra C. Characterization of five associations of F8 missense mutations containing FVIII B domain mutations. Haemophilia. 2016;22:583–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

