Predictors of mortality, ICU hospitalization, and extrapulmonary complications in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34242842
- PMCID: PMC8260549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idnow.2021.07.002
Predictors of mortality, ICU hospitalization, and extrapulmonary complications in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Objective: A major coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak occurred in Northeastern France in spring 2020. This single-center retrospective observational cohort study aimed to compare patients with severe COVID-19 and those with non-severe COVID-19 (survivors vs. non-survivors, ICU patients vs. non-ICU patients) and to describe extrapulmonary complications.
Patients and methods: We included all patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 admitted to Colmar Hospital in March 2020.
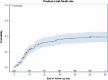
Results: We examined 600 patients (median age 71.09 years; median body mass index: 26.9 kg/m2); 57.7% were males, 86.3% had at least one comorbidity, 153 (25.5%) required ICU hospitalization, and 115 (19.1%) died. Baseline independent factors associated with death were older age (>75 vs. ≤75 years), male sex, oxygen supply, chronic neurological, renal, and pulmonary diseases, diabetes, cancer, low platelet and hemoglobin counts, and high levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and serum creatinine. Factors associated with ICU hospitalization were age <75 years, oxygen supply, chronic pulmonary disease, absence of dementia, and high levels of CRP, hemoglobin, and serum creatinine. Among the 600 patients, 80 (13.3%) had an acute renal injury, 33 (5.5%) had a cardiovascular event, 27 (4.5%) had an acute liver injury, 24 (4%) had venous thromboembolism, eight (1.3%) had a neurological event, five (0.8%) had rhabdomyolysis, and one had acute pancreatitis. Most extrapulmonary complications occurred in ICU patients.
Conclusion: This study highlighted the main risk factors for ICU hospitalization and death caused by severe COVID-19 and the frequency of numerous extrapulmonary complications in France.
Keywords: COVID-19; Extrapulmonary COVID-19; Mortality; Outcome; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Li Y., Wang M., Zhou Y., Chang J., Xian Y., Mao L., et al. 2020. Acute Cerebrovascular Disease Following COVID-19: A Single Center, Retrospective, Observational Study. [htpps://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3550025. preprint] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

