Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Selectively Protects the Heart in Response to Metabolic Stress
- PMID: 34244238
- PMCID: PMC8576508
- DOI: 10.2337/db20-1212
Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Selectively Protects the Heart in Response to Metabolic Stress
Abstract
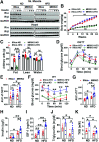
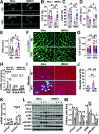
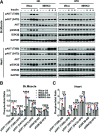
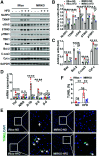
Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are the leading causes of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Although insulin resistance is believed to underlie these disorders, anecdotal evidence contradicts this common belief. Accordingly, obese patients with cardiovascular disease have better prognoses relative to leaner patients with the same diagnoses, whereas treatment of T2DM patients with thiazolidinedione, one of the popular insulin-sensitizer drugs, significantly increases the risk of heart failure. Using mice with skeletal musclespecific ablation of the insulin receptor gene (MIRKO), we addressed this paradox by demonstrating that insulin signaling in skeletal muscles specifically mediated cross talk with the heart, but not other metabolic tissues, to prevent cardiac dysfunction in response to metabolic stress. Despite severe hyperinsulinemia and aggregating obesity, MIRKO mice were protected from myocardial insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and metabolic reprogramming in response to diet-induced obesity. Consequently, the MIRKO mice were also protected from myocardial inflammation, cardiomyopathy, and left ventricle dysfunction. Together, our findings suggest that insulin resistance in skeletal muscle functions as a double-edged sword in metabolic diseases.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Brüning JC, Michael MD, Winnay JN, et al. . A muscle-specific insulin receptor knockout exhibits features of the metabolic syndrome of NIDDM without altering glucose tolerance. Mol Cell 1998;2:559–569 - PubMed
-
- Lavie CJ, Alpert MA, Arena R, Mehra MR, Milani RV, Ventura HO. Impact of obesity and the obesity paradox on prevalence and prognosis in heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2013;1:93–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

