[Spinal ozone therapy]
- PMID: 34244811
- PMCID: PMC8328893
- DOI: 10.1007/s00117-021-00878-4
[Spinal ozone therapy]
Abstract
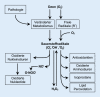
Clinical/methodological problem: Technical advances in the field of spinal interventional neuroradiology allow the application of a wide range of targeted, minimally invasive treatment options including targeted spinal ozone therapy for back pain. This article provides an overview of the biochemical, molecular, immunologic, and pharmaceutical mechanisms and delivery techniques of targeted ozone therapy.
Standard radiological methods: Computed tomography (CT), conventional X‑ray (fluoroscopy).
Performance: Computed tomography-guided interventions (epidural, periradicular, facet joint, and intradiscal) have the highest place value and have historically prevailed. Fluoroscopy-guided procedures may also be used.
Practical recommendations: Ozone therapy provides promising results. The article is intended to provide information on the basics of the technique(s).
Zusammenfassung: KLINISCHES/METHODISCHES PROBLEM: Technische Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der spinalen interventionellen Neuroradiologie ermöglichen es, eine breite Palette an gezielten, minimal-invasiven Behandlungsoptionen einschließlich der spinalen Ozontherapie beim Rückenschmerz anzuwenden. Dieser Beitrag gibt eine Übersicht der biochemischen, molekularen, immunologischen und pharmazeutischen Mechanismen sowie Applikationstechniken der gezielten Ozontherapie.
Radiologische standardverfahren: Zum Einsatz kommen die Computertomographie (CT) sowie konventionelle Röntgenaufnahmen (Durchleuchtung). LEISTUNGSFäHIGKEIT: Die CT-gesteuerten Interventionen (epidural, periradikuläre, Facettengelenk und intradiskal) haben den höchsten Stellenwert und haben sich historisch durchgesetzt. Durchleuchtungsgesteuerte Verfahren können ebenfalls eingesetzt werden.
Schlussfolgerung: Die Ozontherapie liefert vielversprechende Ergebnisse. Der Beitrag soll dazu dienen, Informationen über die Grundlagen dieser Technik(en) zu vermitteln.
Keywords: Back pain; Interventional neuroradiology; Ozone; Pain therapy; Spinal surgery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Similar articles
-
[MR-Guided pain therapy: principles and clinical applications].Rofo. 2007 Sep;179(9):914-24. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-963200. Rofo. 2007. PMID: 17705114 Review. German.
-
Imaging-guided injection techniques with fluoroscopy and CT for spinal pain management.Radiographics. 2001 Jul-Aug;21(4):927-39; discussion 940-2. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.21.4.g01jl15927. Radiographics. 2001. PMID: 11452067 Review.
-
An update of comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for interventional techniques in chronic spinal pain. Part II: guidance and recommendations.Pain Physician. 2013 Apr;16(2 Suppl):S49-283. Pain Physician. 2013. PMID: 23615883
-
Intradiscal ozone therapy: fluoroscopic guidance reduces operative time in comparison with CT guidance in patients with lumbar disc herniation.Radiol Med. 2022 May;127(5):526-533. doi: 10.1007/s11547-022-01469-6. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 35290568
-
Medical ozone therapy in facet joint syndrome: an overview of sonoanatomy, ultrasound-guided injection techniques and potential mechanism of action.Med Gas Res. 2021 Oct-Dec;11(4):145-151. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.318859. Med Gas Res. 2021. PMID: 34213496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmidt CO, Kohlmann T. Was wissen wir über das Symptom Rückenschmerz? Epidemiologische Ergebnisse zu Prävalenz, Inzidenz, Verlauf, Risikofaktoren [What do we know about the symptoms of back pain? Epidemiological results on prevalence, incidence, progression and risk factors. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2005;143(3):292–298. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-836631. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schmidt CO, Kohlmann T. Rückenschmerzen in Deutschland – ein epidemiologischer überblick. Klinikarts. 2007;36:680–684. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021785. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical