Neurokinin Receptor 1 (NK1R) Antagonist Aprepitant Enhances Hematoma Clearance by Regulating Microglial Polarization via PKC/p38MAPK/NFκB Pathway After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice
- PMID: 34244927
- PMCID: PMC8608951
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-021-01077-8
Neurokinin Receptor 1 (NK1R) Antagonist Aprepitant Enhances Hematoma Clearance by Regulating Microglial Polarization via PKC/p38MAPK/NFκB Pathway After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice
Abstract
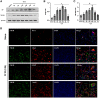
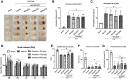
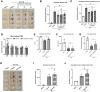
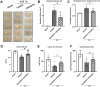
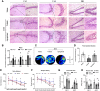
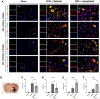
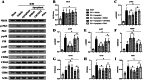
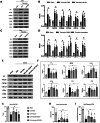
Hematoma clearance is an important therapeutic target to improve outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Recent studies showed that Neurokinin receptor-1 (NK1R) inhibition exerts protective effects in various neurological disease models, but its role in ICH has not been explored. The objective of this study was to investigate the role of NK1R and its relation to hematoma clearance after ICH using an autologous blood injection mouse model. A total of 332 adult male CD1 mice were used. We found that the expression levels of NK1R and its endogenous ligand, substance P (SP), were significantly upregulated after ICH. Intraperitoneal administration of the NK1R selective antagonist, Aprepitant, significantly improved neurobehavior, reduced hematoma volume and hemoglobin levels after ICH, and promoted microglia polarization towards M2 phenotype. Aprepitant decreased phosphorylated PKC, p38MAPK, and NFκB p65, and downregulated M1 markers while upregulating M2 markers after ICH. Intracerebroventricular administration of the NK1R agonist, GR73632 or PKC agonist, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) reversed the effects of Aprepitant. To demonstrate the upstream mediator of NK1R activation, we performed thrombin injection and found that it increased SP. Inhibiting thrombin suppressed SP and decreased M1 markers while increasing M2 microglia polarization. Thus, NK1R inhibition promoted hematoma clearance after ICH by increasing M2 microglial polarization via downregulating PKC/p38MAPK/NFκB signaling pathway, and thrombin may be a key upstream mediator of NK1R activation. Therapeutic interventions inhibiting NK1R signaling may be a new target for the treatment of ICH.
Keywords: Hematoma clearance; Intracerebral hemorrhage; Microglia polarization; Neurokinin receptor-1; Thrombin.
© 2021. The American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aprepitant attenuates NLRC4-dependent neuronal pyroptosis via NK1R/PKCδ pathway in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Aug 3;19(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02558-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35922848 Free PMC article.
-
HO-1 represses NF-κB signaling pathway to mediate microglia polarization and phagocytosis in intracerebral hemorrhage.Neuroscience. 2025 Feb 6;566:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.12.020. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 39672459
-
Recombinant CCL17 Enhances Hematoma Resolution and Activation of CCR4/ERK/Nrf2/CD163 Signaling Pathway After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Oct;17(4):1940-1953. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00908-4. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32783091 Free PMC article.
-
Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage.Nat Rev Neurol. 2017 Jul;13(7):420-433. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.69. Epub 2017 May 19. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28524175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurokinin-1 receptor in addictive processes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Oct;351(1):2-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.210799. Epub 2014 Jul 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 25038175 Review.
Cited by
-
Mas receptor activation facilitates innate hematoma resolution and neurological recovery after hemorrhagic stroke in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Apr 24;21(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03105-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38658922 Free PMC article.
-
Application Effect of Whole-Process Seamless Nursing Model Based on Smart Healthcare Mode in Perioperative Period of Patients Undergoing Hematoma Removal.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Feb 23;2022:1323678. doi: 10.1155/2022/1323678. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35251559 Free PMC article.
-
Catalpalactone protects rats nerve function from hypoxic lesion by polarizing microglial cells toward M2 phenotype.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 12;30(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02321-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39940010 Free PMC article.
-
Aprepitant Inhibits JNK and p38/MAPK to Attenuate Inflammation and Suppresses Inflammatory Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 11;12:811584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.811584. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35087409 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of LRP6 with HLY78 Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via GSK3β/Sirt1/PGC-1α Pathway after ICH.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 4;2022:7542468. doi: 10.1155/2022/7542468. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35419167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schrag M, Kirshner H. Management of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: JACC Focus Seminar. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(15):1819–1831. - PubMed
-
- Corbett D, Carmichael ST, Murphy TH, Jones TA, Schwab ME, Jolkkonen J, et al. Enhancing the Alignment of the Preclinical and Clinical Stroke Recovery Research Pipeline: Consensus-Based Core Recommendations From the Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable Translational Working Group. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017;31(8):699–707. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang J, Peng Y, Gu C, Chen H, Lin Z, Zhou H, et al. Wogonin Accelerates Hematoma Clearance and Improves Neurological Outcome via the PPAR-gamma Pathway After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

