[Immunotherapy adaptation in lung cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic]
- PMID: 34246519
- PMCID: PMC8241593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmr.2021.06.005
[Immunotherapy adaptation in lung cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic]
Abstract
Introduction: COVID-19 pandemics required changes in medical practices. In thoracic oncology, pembrolizumab was doubled to 400mg every 6weeks, nivolumab to 480mg every 4weeks. The objective of our study was to assess the impact on quality of life, and on psychological state, as well as the tolerance, of this new schedule.
Methods: Thoracic oncologic patients who underwent these therapeutic changes in our center during the first COVID-19 epidemic wave were included. Their quality of life was assessed using the Quality of Life Questionnaire-30, their psychological state by the Hospital Anxiety Depression (HAD) scale. We also reported the preferred administration schedule, as well as adverse events.
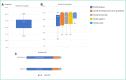
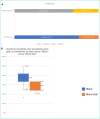
Results: Thirty patients were included. The overall quality of life was preserved. Rates on HAD scale were low. Tolerance was acceptable. In majority, patients preferred the new procedure. They had a significantly better quality of life compared to those who preferred the old one.
Conclusions: This new immunotherapy schedule in thoracic oncology is well tolerated and allows a preservation of quality of life. This therapeutic option may be favored in the context of COVID-19 pandemics.
Introduction: La première vague de COVID-19 a nécessité des modifications des pratiques médicales selon les recommandations des sociétés savantes. En oncologie thoracique, le pembrolizumab a été doublé à 400 mg toutes les 6 semaines, le nivolumab à 480 mg toutes les 4 semaines. L’objectif de notre étude était d’évaluer l’impact sur la qualité de vie, l’état psychologique et la tolérance de ce nouveau schéma d’administration.
Méthodes: Durant la première vague, nous avons inclus des patients suivis en oncologie thoracique chez qui le schéma d’administration de l’immunothérapie avait été modifié et utilisé le Quality of Life Questionnaire-30 pour mesurer leur qualité de vie et l’échelle Hospital Anxiety Depression (HAD) pour évaluer l’état psychologique. Nous avons également précisé les préférences des patients concernant le schéma d’administration et les effets indésirables présentés.
Résultats: Chez les 30 patients inclus la qualité de vie globale était conservée (score médian 75 [33–100]), les scores HAD étaient < 8 chez 23/30 patients pour la dépression, 22/30 pour celui d’anxiété. La tolérance était acceptable. Vingt et un sur 30 patients préféraient le nouveau schéma d’administration .
Conclusions: Ce nouveau schéma d’administration d’immunothérapie a montré une bonne tolérance avec une qualité de vie préservée. Cela est une option thérapeutique possible en contexte de pandémie.
Keywords: COVID-19; Carcinome bronchique non à petites cellules; Immunotherapy; Immunothérapie; Non-small cell lung cancer; Quality of life; Qualité de vie; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV2.
Copyright © 2021 SPLF. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Actualités GOLF – Société de pneumologie de langue française [Internet]. [cité 3 nov 2020. Disponible sur : https://splf.fr/actualites-golf/].
-
- CT-17862_KEYTRUDA_PIS_RCP_Avis1_CT17862.pdf [Internet]. [cité 7 nov 2020. Disponible sur : https://www.has-sante.fr/upload/docs/evamed/CT-17862_KEYTRUDA_PIS_RCP_Av...].
-
- Lala M., Li T.R., de Alwis D.P., et al. A six-weekly dosing schedule for pembrolizumab in patients with cancer based on evaluation using modelling and simulation. Eur J Cancer. 2020;131:68–75. - PubMed
-
- CT-17114_OPDIVO_QD_INS_Avis1_CT17114.pdf [Internet]. [cité 7 nov 2020. Disponible sur : https://www.has-sante.fr/upload/docs/evamed/CT-17114_OPDIVO_QD_INS_Avis1...].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

