A stacked ensemble for the detection of COVID-19 with high recall and accuracy
- PMID: 34247135
- PMCID: PMC8241584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104608
A stacked ensemble for the detection of COVID-19 with high recall and accuracy
Abstract
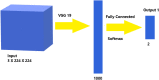
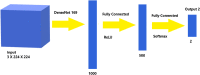
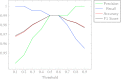
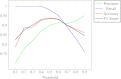
The main challenges for the automatic detection of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from computed tomography (CT) scans of an individual are: a lack of large datasets, ambiguity in the characteristics of COVID-19 and the detection techniques having low sensitivity (or recall). Hence, developing diagnostic techniques with high recall and automatic feature extraction using the available data are crucial for controlling the spread of COVID-19. This paper proposes a novel stacked ensemble capable of detecting COVID-19 from a patient's chest CT scans with high recall and accuracy. A systematic approach for designing a stacked ensemble from pre-trained computer vision models using transfer learning (TL) is presented. A novel diversity measure that results in the stacked ensemble with high recall and accuracy is proposed. The stacked ensemble proposed in this paper considers four pre-trained computer vision models: the visual geometry group (VGG)-19, residual network (ResNet)-101, densely connected convolutional network (DenseNet)-169 and wide residual network (WideResNet)-50-2. The proposed model was trained and evaluated with three different chest CT scans. As recall is more important than precision, the trade-offs between recall and precision were explored in relevance to COVID-19. The optimal recommended threshold values were found for each dataset.
Keywords: COVID-19; False negatives; Recall; Transfer learning.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no known conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Automatic detection of COVID-19 from chest CT scan and chest X-Rays images using deep learning, transfer learning and stacking.Appl Intell (Dordr). 2022;52(2):2243-2259. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02393-4. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Appl Intell (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 34764605 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of COVID-19 using ensemble of transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network based on CT scans.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Jan;16(1):115-123. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02286-w. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33191476 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray image phase features for improved diagnosis of COVID-19 using convolutional neural network.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Feb;16(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02305-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33420641 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(12):1403-1418. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210713113439. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34259149 Review.
Cited by
-
Using Machine Learning to Fight Child Acute Malnutrition and Predict Weight Gain During Outpatient Treatment with a Simplified Combined Protocol.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 6;16(23):4213. doi: 10.3390/nu16234213. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683605 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble deep honey architecture for COVID-19 prediction using CT scan and chest X-ray images.Multimed Syst. 2023 Apr 11:1-27. doi: 10.1007/s00530-023-01072-3. Online ahead of print. Multimed Syst. 2023. PMID: 37360153 Free PMC article.
-
A lightweight CNN-based network on COVID-19 detection using X-ray and CT images.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jul;146:105604. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105604. Epub 2022 May 11. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35576824 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Ensemble Learning-Based Models for Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest CT Images.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jan 15;10(1):166. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10010166. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052328 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-class classification framework for disease screening and disease diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023;82(10):14367-14401. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13710-5. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 36157353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus update (live): 28,988,031 cases and 925,320 deaths from COVID-19 virus pandemic - worldometer.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

