Autocrine GMCSF Signaling Contributes to Growth of HER2+ Breast Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- PMID: 34247146
- PMCID: PMC8986153
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0259
Autocrine GMCSF Signaling Contributes to Growth of HER2+ Breast Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
Abstract
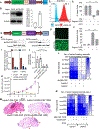
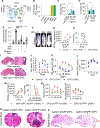
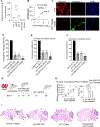
Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LC) occurs when tumor cells spread to the cerebrospinal fluid-containing leptomeninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. LC is an ominous complication of cancer with a dire prognosis. Although any malignancy can spread to the leptomeninges, breast cancer, particularly the HER2+ subtype, is its most common origin. HER2+ breast LC (HER2+ LC) remains incurable, with few treatment options, and the molecular mechanisms underlying proliferation of HER2+ breast cancer cells in the acellular, protein, and cytokine-poor leptomeningeal environment remain elusive. Therefore, we sought to characterize signaling pathways that drive HER2+ LC development as well as those that restrict its growth to leptomeninges. Primary HER2+ LC patient-derived ("Lepto") cell lines in coculture with various central nervous system (CNS) cell types revealed that oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPC), the largest population of dividing cells in the CNS, inhibited HER2+ LC growth in vitro and in vivo, thereby limiting the spread of HER2+ LC beyond the leptomeninges. Cytokine array-based analyses identified Lepto cell-secreted GMCSF as an oncogenic autocrine driver of HER2+ LC growth. LC/MS-MS-based analyses revealed that the OPC-derived protein TPP1 proteolytically degrades GMCSF, decreasing GMCSF signaling and leading to suppression of HER2+ LC growth and limiting its spread. Finally, intrathecal delivery of neutralizing anti-GMCSF antibodies and a pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor (CCT137690) synergistically inhibited GMCSF and suppressed activity of GMCSF effectors, reducing HER2+ LC growth in vivo. Thus, OPC suppress GMCSF-driven growth of HER2+ LC in the leptomeningeal environment, providing a potential targetable axis. SIGNIFICANCE: This study characterizes molecular mechanisms that drive HER2+ leptomeningeal carcinomatosis and demonstrates the efficacy of anti-GMCSF antibodies and pan-Aurora kinase inhibitors against this disease.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Tabouret E, Chinot O, Metellus P, Tallet A, Viens P, Goncalves A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: an overview. Anticancer Res 2012;32:4655–62 - PubMed
-
- Quigley MR, Fukui O, Chew B, Bhatia S, Karlovits S. The shifting landscape of metastatic breast cancer to the CNS. Neurosurg Rev 2013;36:377–82 - PubMed
-
- Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 2010;28:3271–7 - PubMed
-
- Spector R, Robert Snodgrass S, Johanson CE. A balanced view of the cerebrospinal fluid composition and functions: Focus on adult humans. Exp Neurol 2015;273:57–68 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

