HVEM Promotes the Osteogenesis of allo-MSCs by Inhibiting the Secretion of IL-17 and IFN-γ in Vγ4T Cells
- PMID: 34248977
- PMCID: PMC8261146
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.689269
HVEM Promotes the Osteogenesis of allo-MSCs by Inhibiting the Secretion of IL-17 and IFN-γ in Vγ4T Cells
Abstract
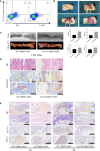
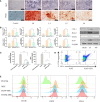
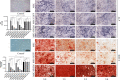
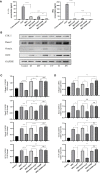
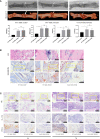
Bone defects are a common orthopaedic concern, and an increasing number of tissue-engineered bones (TEBs) are used to repair bone defects. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (allo-MSCs) are used as seed cells in many approaches to develop TEB constructs, but the immune response caused by allogeneic transplantation may lead to transplant failure. V gamma 4 T (Vγ4T) cells play an important role in mediating the immune response in the early stage after transplantation; therefore, we wanted to verify whether suppressing Vγ4T cells by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM)/B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) signalling can promote MSCs osteogenesis in the transplanted area. In vitro experiments showed that the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs and Vγ4T cells was weakened after co-culture, and an increase in interleukin-17 (IL-17) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) levels was detected in the culture supernatant. HVEM-transfected MSCs (MSCs-HVEM) still exhibited osteogenic differentiation activity after co-culture with Vγ4T cells, and the levels of IL-17 and IFN-γ in the co-culture supernatant were significantly reduced. In vivo experiments revealed that inflammation in the transplanted area was reduced and osteogenic repair was enhanced after Vγ4T cells were removed. MSCs-HVEM can also consistently contribute to reduced inflammation in the transplanted area and enhanced bone repair in wild-type (WT) mice. Therefore, our experiments verified that HVEM can promote the osteogenesis of allo-MSCs by inhibiting IL-17 and IFN-γ secretion from Vγ4T cells.
Keywords: HVEM-BTLA; IL-17; MSc; Tissue engineered bone; Vγ4T cells; immunomodulatory.
Copyright © 2021 He, Xiao, Song, Zhou, Rong, He and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
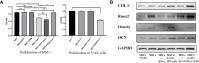
References
-
- Niemeyer P, Fechner K, Milz S, Richter W, Suedkamp N, Mehlhorn A, et al. Comparison of Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue for Bone Regeneration in a Critical Size Defect of the Sheep Tibia and the Influence of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Biomaterials (2010) 31(13):3572–9. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.085 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

