Experimental comparative assay of tensile resistance of greater saphenous vein from ankle and groin
- PMID: 34249114
- PMCID: PMC8244984
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.190117
Experimental comparative assay of tensile resistance of greater saphenous vein from ankle and groin
Abstract
Background: The great saphenous vein is used as patch material in several types of arterial reconstruction, including trauma and carotid and femoral endarterectomy. There have been reports of saphenous patch blowout, particularly of patches constructed with veins harvested from the ankle. There is a need for objective measurement of the resistance of saphenous vein tissues.
Objectives: To measure the tensile strength of the great saphenous vein harvested at the ankle and groin and analyze the correlation between diameter and tissue strength.
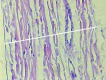
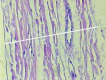
Methods: Venous samples were harvested during elective saphenous stripping in patients with symptomatic varicose veins. Only segments without reflux were included. Ten limbs from eight patients were studied, providing 20 samples in total. Venous segments were opened along their longitudinal axis and fitted to electronic traction assay equipment to obtain values for material maximum tension in kilograms-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm2; the maximum force resisted by the segment, divided by its cross-sectional area).
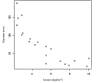
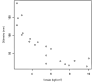
Results: The average maximum tension in the ankle saphenous vein group ranged from 74.02 to 190.10 kgf/cm2 and from 13.53 to 69.45 kgf/cm2 in the groin saphenous vein group (p < 0.0001). The Pearson coefficient for the correlation between vein diameter and maximum tension was -0.852 (moderate to strong inverse correlation).
Conclusions: Ankle saphenous vein tissue from female patients operated for varicose veins has significantly higher resistance than saphenous vein tissue from the groin and there is an inverse relation between vein diameter and resistance of tissue from the same population.
Contexto: A veia safena magna é usada como material de remendo em vários tipos de reconstrução arterial, incluindo no trauma e endarterectomias de carótida e femoral. Houve relatos de ruptura do remendo de safena, particularmente de veias colhidas na região do tornozelo. Há uma necessidade de medição objetiva da resistência tecidual da safena magna.
Objetivos: Mensurar a força tensional suportada pela veia safena magna e analisar a correlação entre resistência e diâmetro da veia.
Métodos: As veias foram coletadas durante operações de safenectomia por varizes dos membros inferiores. Foram analisados apenas segmentos sem refluxo. Foram analisados 10 membros de oito pacientes, com um total de 20 espécimes. Os espécimes foram submetidos a ensaio de tração em equipamento eletrônico, obtendo-se os valores de tensão máxima do material em quilogramas-força por centímetro quadrado (kgf/cm2; força máxima dividida pela área de secção transversa do segmento submetido à tração).
Resultados: A tensão máxima suportada pela veia safena do tornozelo variou de 74,02 a 190,10 kgf/cm2, e a tensão máxima da veia safena da crossa variou de 13,53 a 69,45 kgf/cm2 (p < 0,0001). O coeficiente de correlação de Pearson entre o diâmetro da veia distendida e a tensão máxima suportada foram iguais a -0,852 (correlação inversa moderada a forte).
Conclusões: A resistência tecidual da veia safena magna do tornozelo é maior do que a da crossa em mulheres submetidas a operação de varizes; há correlação negativa entre o diâmetro da veia e sua resistência tecidual nessa mesma população.
Keywords: saphenous vein; varicose veins; vascular surgical procedures; vascular system injuries.
Copyright© 2021 The authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is saphenofemoral junction reconstruction necessary during stripping of the saphenous vein?Surgery. 2006 May;139(5):640-5. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.09.014. Surgery. 2006. PMID: 16701097
-
Resecting the great saphenous stump with endothelial inversion decreases neither neovascularization nor thigh varicosity recurrence.J Vasc Surg. 2008 May;47(5):1028-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.12.039. Epub 2008 Mar 21. J Vasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18358671 Clinical Trial.
-
Selective stripping operation based on Doppler ultrasonic findings for primary varicose veins of the lower extremities.Surgery. 1988 Jun;103(6):615-9. Surgery. 1988. PMID: 3287670
-
A systematic review of the treatment of residual below the knee venous reflux after endovenous thermal ablation of the great saphenous vein.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022 Jan;10(1):233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2021.03.024. Epub 2021 Aug 21. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022. PMID: 34425265
-
Is total abolishment of great saphenous reflux in the invasive treatment of superficial chronic venous insufficiency always necessary?Int Angiol. 2009 Feb;28(1):4-11. Int Angiol. 2009. PMID: 19190549 Review.
References
-
- Miyamotto M, Del Valle CE, Moreira RCR, Timi JRR. Comparative analysis of rupture resistance between glutaraldehyde-treated bovine pericardium and great saphenous vein. J Vasc Bras. 2009;8(2):103–111. doi: 10.1590/S1677-54492009000200003. - DOI
-
- Moreira RCR, Del Valle CE. Trauma venoso. In: Thomaz JB, Belczak CEQ, editors. Tratado de flebologia e linfologia. Vol. 1 Rio de Janeiro: Rubio; 2006. pp. 656–661.
-
- Bond R, Rerkasem K, Naylor AR, Aburahma AF, Rothwell PM. Systematic review of randomized controlled trials of patch angioplasty versus primary closure and different types of patch materials during carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 2004;40(6):1126–1135. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2004.08.048. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
