Genome engineering and disease modeling via programmable nucleases for insulin gene therapy; promises of CRISPR/Cas9 technology
- PMID: 34249224
- PMCID: PMC8246254
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.485
Genome engineering and disease modeling via programmable nucleases for insulin gene therapy; promises of CRISPR/Cas9 technology
Abstract
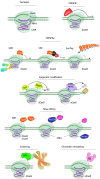
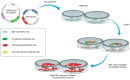
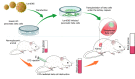
Targeted genome editing is a continually evolving technology employing programmable nucleases to specifically change, insert, or remove a genomic sequence of interest. These advanced molecular tools include meganucleases, zinc finger nucleases, transcription activator-like effector nucleases and RNA-guided engineered nucleases (RGENs), which create double-strand breaks at specific target sites in the genome, and repair DNA either by homologous recombination in the presence of donor DNA or via the error-prone non-homologous end-joining mechanism. A recently discovered group of RGENs known as CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing systems allowed precise genome manipulation revealing a causal association between disease genotype and phenotype, without the need for the reengineering of the specific enzyme when targeting different sequences. CRISPR/Cas9 has been successfully employed as an ex vivo gene-editing tool in embryonic stem cells and patient-derived stem cells to understand pancreatic beta-cell development and function. RNA-guided nucleases also open the way for the generation of novel animal models for diabetes and allow testing the efficiency of various therapeutic approaches in diabetes, as summarized and exemplified in this manuscript.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Diabetes; Disease modeling; Insulin gene therapy; Programmable nucleases; Stem cells.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest for this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

