Exploring the inhibitory potentials of Momordica charantia bioactive compounds against Keap1-Kelch protein using computational approaches
- PMID: 34249600
- PMCID: PMC8233444
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-021-00100-2
Exploring the inhibitory potentials of Momordica charantia bioactive compounds against Keap1-Kelch protein using computational approaches
Abstract
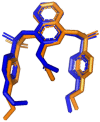
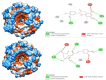
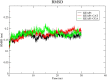
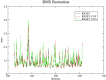
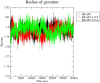
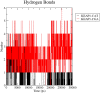
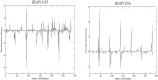
The search for Keap1 inhibitors as potential Nrf2 activator is a way of increasing the antioxidant status of the human cellular environ. In this research, we used in silico methods to investigate Keap1-kelch inhibitory potential of Momordica charantia's bioactive compounds in order to predict their Nrf2 activating potential. ADMET profiling, physicochemical properties, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and Molecular Mechanics-Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area (g_MMPBSA) free energy calculation studies were executed to drive home our aim. Out of all the bioactive compounds of Momordica charantia, catechin (CAT) and chlorogenic acid (CGA) were selected based on their ADMET profile, physicochemical properties, and molecular docking analysis. Molecular docking studies of CAT and CGA to Keap1 kelch domain showed that they have - 9.2 kJ/mol and - 9.1 kJ/mol binding energies respectively with CAT having four hydrogen bond interactions with Keap1 while CGA had three. Analysis after the 30 ns molecular dynamics simulation revealed that CAT and CGA were both stable, although with minimal conformational alterations at the kelch pocket of Keap1. Finally, MMPBSA calculation of the Gibbs free energy of each amino acid interaction with CAT and CGA revealed that CAT had a higher total binding energy than CGA. Therefore, the Keap1 inhibitory capacities and the molecular dynamic characters of CAT and CGA at the Kelch domain of Keap1 suggest a putative Nrf2 signaling activating prowess.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40203-021-00100-2.
Keywords: Keap1; Molecular Mechanics-Poisson Boltzman Surface Area (g_MMPBSA); Molecular dynamics; Momordica charantia.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
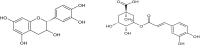
Similar articles
-
Molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics and docking studies of some Keap1 inhibitors - An insight into the atomistic mechanisms of their antioxidant potential.Heliyon. 2021 Jun 16;7(6):e07317. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07317. eCollection 2021 Jun. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34195424 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of intermolecular interactions between chlorogenic acid and glucose-6-phosphate translocase: A step towards chemically induced glycogen storage disease type 1b model.3 Biotech. 2023 Jul;13(7):250. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03661-5. Epub 2023 Jun 26. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37383953 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorogenic acid ameliorates mice clinical endometritis by activating Keap1/Nrf2 and inhibiting NFκB signalling pathway.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 27;73(6):785-795. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab020. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33734387
-
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) drug discovery: Biochemical toolbox to develop NRF2 activators by reversible binding of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1).Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Oct 1;631:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28801166 Review.
-
Direct Keap1-kelch inhibitors as potential drug candidates for oxidative stress-orchestrated diseases: A review on In silico perspective.Pharmacol Res. 2021 May;167:105577. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105577. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33774182 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation revealed promising drug candidates of p53-MDM2 interaction.J Mol Model. 2022 May 10;28(6):142. doi: 10.1007/s00894-022-05131-w. J Mol Model. 2022. PMID: 35536362
-
Phenolic Compounds from Pyrus communis Residues: Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action and Therapeutic Applications.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Mar 8;14(3):280. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14030280. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reinstating apoptosis using putative Bcl-xL natural product inhibitors: Molecular docking and ADMETox profiling investigations.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022 Nov 14;18(3):461-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.10.014. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36818176 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric activation of AMPK ADaM's site by structural analogs of Epigallocatechin and Galegine: computational molecular modeling investigation.In Silico Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;13(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s40203-025-00311-x. eCollection 2025. In Silico Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39896884
-
Therapeutic Potential of Momordicine I from Momordica charantia: Cardiovascular Benefits and Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10518. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910518. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakare R, Magbagbeola O, Okunowo MPR. Nutritional and chemical evaluation of Momordica charantia. J Med Plant Res. 2010;4:2189–2193.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

