Efficacy of Ebselen Against Invasive Aspergillosis in a Murine Model
- PMID: 34249777
- PMCID: PMC8260993
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.684525
Efficacy of Ebselen Against Invasive Aspergillosis in a Murine Model
Abstract
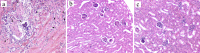
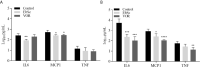
Invasive aspergillosis is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality among invasive fungal infections. The search for new antifungal drugs becomes imperative when existing drugs are not able to efficiently treat these infections. Ebselen, is an organoselenium compound, already successfully approved in clinical trials as a repositioned drug for the treatment of bipolar disorder and prevention of noise-induced hearing loss. In this study, we aimed to reposition ebselen for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis by showing ebselen effectiveness in a murine model. For this, BALB/c mice were immunosuppressed and infected systemically with Aspergillus fumigatus. Animals were divided and treated with ebselen, voriconazole, or drug-free control, for four days. The kidneys were used for CFU count and, histopathological and cytokine analysis. Ebselen was able to significantly reduce the fungal burden in the kidneys of infected mice with efficacy comparable with voriconazole treatment as both had reductions to the same extent. The absence of hyphae and intact kidney tissue structure observed in the histopathological sections analyzed from treated groups corroborate with the downregulation of IL-6 and TNF. In summary, this study brings for the first time in vivo evidence of ebselen efficacy against invasive aspergillosis. Despite these promising results, more animal studies are warranted to evaluate the potential role of ebselen as an alternative option for the management of invasive aspergillosis in humans.
Keywords: Aspergillus; antifungal; ebselen; murine model; systemic infection.
Copyright © 2021 Sakita, Capoci, Conrado, Rodrigues-Vendramini, Faria, Arita, Becker, Bonfim-Mendonça, Svidzinski and Kioshima.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Øya E., Becher R., Ekeren L., Afanou A. K. J., Øvrevik J., Holme J. A. (2019). Pro-Inflammatory Responses in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Induced by Spores and Hyphal Fragments of Common Damp Indoor Molds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16 (6), 1085. 10.3390/ijerph16061085 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho S. Y., Lee D. G., Kim W. B., Chun H. S., Park C., Myong J. P., et al. . (2019). Epidemiology and Antifungal Susceptibility Profile of Aspergillus Species: Comparison Between Environmental and Clinical Isolates From Patients With Hematologic Malignancies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 57 (7), e02023–e02018. 10.1128/JCM.02023-18 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ClinicalTrials.gov (2020). Identifier NCT04484025, Spi-1005 Treatment in Moderate Covid-19 Patients (Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine US; ). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04484025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

