Detrimental Effect of Various Preparations of the Human Amniotic Membrane Homogenate on the 2D and 3D Bladder Cancer In vitro Models
- PMID: 34249888
- PMCID: PMC8267883
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.690358
Detrimental Effect of Various Preparations of the Human Amniotic Membrane Homogenate on the 2D and 3D Bladder Cancer In vitro Models
Abstract
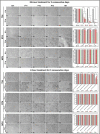
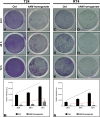
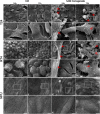
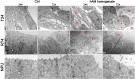
Despite being among the ten most common cancers with high recurrence rates worldwide, there have been no major breakthroughs in the standard treatment options for bladder cancer in recent years. The use of a human amniotic membrane (hAM) to treat cancer is one of the promising ideas that have emerged in recent years. This study aimed to investigate the anticancer activity of hAM homogenate on 2D and 3D cancer models. We evaluated the effects of hAM homogenates on the human muscle invasive bladder cancer urothelial (T24) cells, papillary cancer urothelial (RT4) cells and normal porcine urothelial (NPU) cells as well as on human mammary gland non-tumorigenic (MCF10a) cells and low-metastatic breast cancer (MCF7) cells. After 24 h, we observed a gradual detachment of cancerous cells from the culture surface, while the hAM homogenate did not affect the normal cells. The most pronounced effect hAM homogenate had on bladder cancer cells; however, the potency of their detachment was dependent on the treatment protocol and the preparation of hAM homogenate. We demonstrated that hAM homogenate significantly decreased the adhesion, growth, and proliferation of human bladder invasive and papillary cancer urothelial cells and did not affect normal urothelial cells even in 7-day treatment. By using light and electron microscopy we showed that hAM homogenate disrupted the architecture of 2D and 3D bladder cancer models. The information provided by our study highlights the detrimental effect of hAM homogenate on bladder cancer cells and strengthens the idea of the potential clinical application of hAM for bladder cancer treatment.
Keywords: 2D and 3D in vitro models; cancer; cell cycle; light and electron microscopy; proliferation; urothelium.
Copyright © 2021 Janev, Ramuta, Tratnjek, Sardoč, Obradović, Mojsilović, Taskovska, Smrkolj and Kreft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration (2005a). Adjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration. Eur. Urol. 48 189–199; discussion 199–201. - PubMed
-
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration (2005b). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur. Urol. 48 202–205; discussion 205–206. - PubMed
-
- Apolo A. B., Infante J. R., Balmanoukian A., Patel M. R., Wang D., Kelly K., et al. (2017). Avelumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 antibody, in patients with refractory metastatic urothelial carcinoma: results from a multicenter, phase Ib study. J. Clin. Oncol. 35 2117–2124. 10.1200/jco.2016.71.6795 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balar A. V., Galsky M. D., Rosenberg J. E., Powles T., Petrylak D. P., Bellmunt J., et al. (2017). Atezolizumab as first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 389 67–76. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

