Cadaverine regulates biotin synthesis to modulate primary root growth in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 34250670
- PMCID: PMC8518694
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.15417
Cadaverine regulates biotin synthesis to modulate primary root growth in Arabidopsis
Abstract
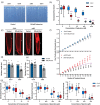
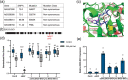
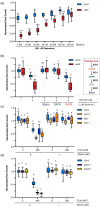
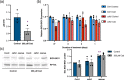
Cadaverine, a polyamine, has been linked to modification of root growth architecture and response to environmental stresses in plants. However, the molecular mechanisms that govern the regulation of root growth by cadaverine are largely unexplored. Here we conducted a forward genetic screen and isolated a mutation, cadaverine hypersensitive 3 (cdh3), which resulted in increased root-growth sensitivity to cadaverine, but not other polyamines. This mutation affects the BIO3-BIO1 biotin biosynthesis gene. Exogenous supply of biotin and a pathway intermediate downstream of BIO1, 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid, suppressed this cadaverine sensitivity phenotype. An in vitro enzyme assay showed cadaverine inhibits the BIO3-BIO1 activity. Furthermore, cadaverine-treated seedlings displayed reduced biotinylation of Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein 1 of the acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase complex involved in de novo fatty acid biosynthesis, resulting in decreased accumulation of triacylglycerides. Taken together, these results revealed an unexpected role of cadaverine in the regulation of biotin biosynthesis, which leads to modulation of primary root growth of plants.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; biotin; cadaverine; polyamines; root architecture.
© 2021 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Smelly business - Cadaverine modulates root growth by inhibiting biotin synthesis.Plant J. 2021 Sep;107(5):1281-1282. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15471. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 34535941 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alban, C. , Job, D. & Douce, R. (2000) Biotin metabolism in plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 51, 17–47. - PubMed
-
- Aubert, S. , Alban, C. , Bligny, R. & Douce, R. (1996) Induction of beta‐methylcrotonyl‐coenzyme A carboxylase in higher plant cells during carbohydrate starvation: evidence for a role of MCCase in leucine catabolism. FEBS Letters, 383, 175–180. - PubMed
-
- Aziz, A. , Martin‐Tanguy, J. & Larher, F. (1998) Stress‐induced changes in polyamine and tyramine levels can regulate proline accumulation in tomato leaf discs treated with sodium chloride. Physiologia Plantarum, 104, 195–202. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Aziz_Aziz3/publication/225274396_St....
-
- Batchelor, R. , Sarkez, A. , Cox, W.G. & Johnson, I. (2007) Fluorometric assay for quantitation of biotin covalently attached to proteins and nucleic acids. BioTechniques, 43, 503–507. https://doi.org/10.2144/000112564. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

