Adolescent depressed mood and difficulties with emotion regulation: Concurrent trajectories of change
- PMID: 34252783
- PMCID: PMC8380718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2021.07.001
Adolescent depressed mood and difficulties with emotion regulation: Concurrent trajectories of change
Abstract
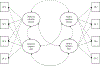
Introduction: Adolescent depression is a significant mental health concern. Emotion regulation difficulties have been associated with subsequent depressive symptoms, though different facets of emotion regulation are rarely compared. This study examined the degree to which trajectories of change in different facets of emotion regulation (goal-directed behavior, impulse control, and regulation strategies) and depressive symptoms were associated across twelve months in a clinical adolescent sample.
Methods: Participants included 110 adolescents from the US who were enrolled in a randomized trial that tested a cognitive-behavioral treatment for youth with co-occurring mental health and substance use concerns (Mage = 15.71 years; 57.3% male). Assessments were conducted at baseline, 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-ups. Three separate bivariate latent basis growth curve analyses were conducted. Correlations between latent intercepts and latent slopes, as well as overall model fit, were examined.
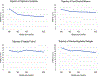
Results: Impulse control and goal-directed behavior were each associated with depressive symptoms at baseline. Additionally, change in impulse control over time was significantly associated with change in depressive symptoms. However, the same was not true for goal-directed behavior. Overall fit indices for models of emotion regulation strategies were below acceptable levels and thus could not be interpreted.
Conclusions: Findings from the present study indicate that adolescents' depressive symptoms appear to improve as their perceived ability to control impulses improves. These results suggest that addressing impulse control difficulties may be an important step in treating adolescent depression and co-occurring disorders.
Keywords: Adolescence; Depression; Emotion regulation; Impulse control.
Copyright © 2021 The Foundation for Professionals in Services for Adolescents. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sexual Identity and its Association with Trajectories of Depressive Symptoms and Emotion Regulation Difficulties from Early to Middle Adolescence.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2022 Oct;53(5):1062-1074. doi: 10.1007/s10578-021-01188-5. Epub 2021 May 21. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2022. PMID: 34021440 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and Emotion Regulation Difficulties Contribute to Depression in Young Adults With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.Psychol Rep. 2021 Apr;124(2):596-610. doi: 10.1177/0033294120918803. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Psychol Rep. 2021. PMID: 32316842 Free PMC article.
-
Daily Associations between Emotions and Aggressive and Depressive Symptoms in Adolescence: The Mediating and Moderating Role of Emotion Dysregulation.J Youth Adolesc. 2019 Nov;48(11):2207-2221. doi: 10.1007/s10964-019-01071-6. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Youth Adolesc. 2019. PMID: 31302795 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in emotion regulation strategies during the pandemic: prospective pathways to adolescent depressive symptoms.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2024 Dec;65(12):1638-1647. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.14027. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38837359
-
Cognitive deficits in bipolar disorders: Implications for emotion.Clin Psychol Rev. 2018 Feb;59:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29195773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Group Impromptu Music Therapy on Emotional Regulation and Depressive Symptoms of College Students: A Randomized Controlled Study.Front Psychol. 2022 Mar 31;13:851526. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.851526. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35432107 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between social anxiety and sleep quality in depressed adolescents: the mediating role of internet addiction.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 10;15:1416130. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1416130. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39465053 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating role of social connectedness and negative cognitive emotion regulation in the association between problematic Internet use and depression among adolescents.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 26;12:1416073. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1416073. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39391162 Free PMC article.
-
The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation characteristics in depressed adolescents with suicide attempts: a resting-state fMRI study.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 28;14:1228260. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1228260. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37575559 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Impulsivity in Addictive Disorders: a Narrative Review.Curr Addict Rep. 2023 Sep;10(3):485-493. doi: 10.1007/s40429-023-00491-6. Epub 2023 May 13. Curr Addict Rep. 2023. PMID: 38269068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardeen JR, Fergus TA, & Orcutt HK (2012). An examination of the latent structure of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 34, 382–392. 10.1007/s10862-012-9280-y - DOI
-
- Benjamini Y, & Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

