Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms
- PMID: 34253862
- PMCID: PMC8273570
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00649-0
Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms
Abstract
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays a crucial role in host defense against infection and tissue injuries and is a bioindicator of multiple distinct types of cytokine storms. In this review, we present the current understanding of the diverse roles of IL-6, its receptors, and its signaling during acute severe systemic inflammation. IL-6 directly affects vascular endothelial cells, which produce several types of cytokines and chemokines and activate the coagulation cascade. Endothelial cell dysregulation, characterized by abnormal coagulation and vascular leakage, is a common complication in cytokine storms. Emerging evidence indicates that a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, can effectively block IL-6 signaling and has beneficial effects in rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile systemic idiopathic arthritis, and Castleman's disease. Recent work has also demonstrated the beneficial effect of tocilizumab in chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy-induced cytokine storms as well as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Here, we highlight the distinct contributions of IL-6 signaling to the pathogenesis of several types of cytokine storms and discuss potential therapeutic strategies for the management of cytokine storms, including those associated with sepsis and COVID-19.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.K. holds a patent for tocilizumab and has received royalties for Actemra.
Figures
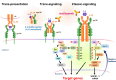
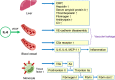


References
-
- Ferrara JL, Abhyankar S, Gilliland DG. Cytokine storm of graft-versus-host disease: a critical effector role for interleukin-1. Transpl. Proc. 1993;25:1216–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

