99mTc-DPD scintigraphy in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) cardiac amyloidosis
- PMID: 34254119
- PMCID: PMC8527328
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jeab095
99mTc-DPD scintigraphy in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) cardiac amyloidosis
Abstract
Aims: Technetium-99m-labelled 3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (99mTc-DPD scintigraphy) is recognized as highly accurate for the non-invasive diagnosis of transthyretin (ATTR) cardiac amyloidosis (CA). A proportion of patients with immunoglobulin light chain (AL) CA have also been reported to show cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake. Herein, we assessed the frequency and degree of cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake and its clinical significance among patients with AL CA.
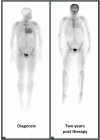
Methods and results: Between 2010 and 2017, 292 consecutive patients with AL CA underwent 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy and were included in this study: 114 (39%) had cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake: grade 1 in 75%, grade 2 in 17%, and grade 3 in 8% of cases. Patients with cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake had poorer cardiac systolic function and higher N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide. No differences were noted in cardiac magnetic resonance parameters between patients with and without cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake (N = 19 and 42, respectively). Patients with cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake showed a trend to worse survival than those with no uptake (log-rank P = 0.056). Among 22 patients who underwent serial 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy, 5 (23%) showed reduction in the grade of cardiac uptake.
Conclusions: In this large cohort of patients with AL CA, 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy ∼40% of cases showed cardiac uptake, including grade 2-3 in 10% of all patients (25% of those with cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake). Cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake was associated with poorer cardiac function and outcomes. These data highlight the critical importance of ruling out AL amyloidosis in all patients with cardiac 99mTc-DPD uptake to ensure such patients are not assumed to have ATTR CA.
Keywords: 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy; amyloidosis; cardiomyopathy; diagnosis; light chain; prognosis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Merlini G, Dispenzieri A, Sanchorawala V, Schönland SO, Palladini G, Hawkins PN. et al. Systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4:38. - PubMed
-
- Ravichandran S, Lachmann HJ, Wechalekar AD.. Epidemiologic and survival trends in amyloidosis, 1987-2019. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1567–8. - PubMed
-
- Falk RH, Alexander KM, Liao R, Dorbala S.. AL (light-chain) cardiac amyloidosis: a review of diagnosis and therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68:1323–41. - PubMed
-
- Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Lacy MQ, Burritt MF, Therneau TM. et al. Serum cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide: a staging system for primary systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:3751–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

