The added value of PSMA PET/MR radiomics for prostate cancer staging
- PMID: 34255130
- PMCID: PMC8803696
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-021-05430-z
The added value of PSMA PET/MR radiomics for prostate cancer staging
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the performance of combined PET and multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) radiomics for the group-wise prediction of postsurgical Gleason scores (psGSs) in primary prostate cancer (PCa) patients.
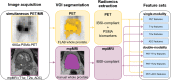
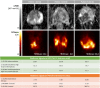
Methods: Patients with PCa, who underwent [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI followed by radical prostatectomy, were included in this retrospective analysis (n = 101). Patients were grouped by psGS in three categories: ISUP grades 1-3, ISUP grade 4, and ISUP grade 5. mpMRI images included T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map. Whole-prostate segmentations were performed on each modality, and image biomarker standardization initiative (IBSI)-compliant radiomic features were extracted. Nine support vector machine (SVM) models were trained: four single-modality radiomic models (PET, T1w, T2w, ADC); three PET + MRI double-modality models (PET + T1w, PET + T2w, PET + ADC), and two baseline models (one with patient data, one image-based) for comparison. A sixfold stratified cross-validation was performed, and balanced accuracies (bAcc) of the predictions of the best-performing models were reported and compared through Student's t-tests. The predictions of the best-performing model were compared against biopsy GS (bGS).
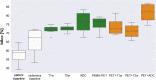
Results: All radiomic models outperformed the baseline models. The best-performing (mean ± stdv [%]) single-modality model was the ADC model (76 ± 6%), although not significantly better (p > 0.05) than other single-modality models (T1w: 72 ± 3%, T2w: 73 ± 2%; PET: 75 ± 5%). The overall best-performing model combined PET + ADC radiomics (82 ± 5%). It significantly outperformed most other double-modality (PET + T1w: 74 ± 5%, p = 0.026; PET + T2w: 71 ± 4%, p = 0.003) and single-modality models (PET: p = 0.042; T1w: p = 0.002; T2w: p = 0.003), except the ADC-only model (p = 0.138). In this initial cohort, the PET + ADC model outperformed bGS overall (82.5% vs 72.4%) in the prediction of psGS.
Conclusion: All single- and double-modality models outperformed the baseline models, showing their potential in the prediction of GS, even with an unbalanced cohort. The best-performing model included PET + ADC radiomics, suggesting a complementary value of PSMA-PET and ADC radiomics.
Keywords: Gleason score; PET/MRI; PSMA; Prostate cancer; Radiomics.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
The role of [18F]-DCFPyL PET/MRI radiomics for pathological grade group prediction in prostate cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jun;50(7):2167-2176. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06136-0. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36809425
-
Role of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET radiomics to predict post-surgical ISUP grade in primary prostate cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul;50(8):2548-2560. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06187-3. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36933074
References
-
- Fendler WP, Eiber M, Beheshti M, Bomanji J, Ceci F, Cho S, Giesel F, Haberkorn U, Hope TA, Kopka K, Krause BJ, Mottaghy FM, Schöder H, Sunderland J, Wan S, Wester HJ, Fanti S, Herrmann K. Joint EANM and SNMMI procedure guideline for prostate cancer imaging: version 1.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(6):1014–1024. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3670-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maurer T, Gschwend JE, Rauscher I, Souvatzoglou M, Haller B, Weirich G, Wester HJ, Heck M, Kübler H, Beer AJ, Schwaiger M, Eiber M. Diagnostic efficacy of (68)gallium-PSMA positron emission tomography compared to conventional imaging for lymph node staging of 130 consecutive patients with intermediate to high risk prostate cancer. J Urol. 2016;195(5):1436–1443. doi: 10.1016/j.juro. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

