Basic principles of biobanking: from biological samples to precision medicine for patients
- PMID: 34255145
- PMCID: PMC8275637
- DOI: 10.1007/s00428-021-03151-0
Basic principles of biobanking: from biological samples to precision medicine for patients
Abstract
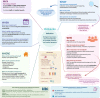
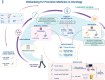
The term "biobanking" is often misapplied to any collection of human biological materials (biospecimens) regardless of requirements related to ethical and legal issues or the standardization of different processes involved in tissue collection. A proper definition of biobanks is large collections of biospecimens linked to relevant personal and health information (health records, family history, lifestyle, genetic information) that are held predominantly for use in health and medical research. In addition, the International Organization for Standardization, in illustrating the requirements for biobanking (ISO 20387:2018), stresses the concept of biobanks being legal entities driving the process of acquisition and storage together with some or all of the activities related to collection, preparation, preservation, testing, analysing and distributing defined biological material as well as related information and data. In this review article, we aim to discuss the basic principles of biobanking, spanning from definitions to classification systems, standardization processes and documents, sustainability and ethical and legal requirements. We also deal with emerging specimens that are currently being generated and shaping the so-called next-generation biobanking, and we provide pragmatic examples of cancer-associated biobanking by discussing the process behind the construction of a biobank and the infrastructures supporting the implementation of biobanking in scientific research.
Keywords: Biobanking; Biospecimens; Cell lines; Preanalytical phase; Standardization; Tissue specimens.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Park A (2009) Biobanks - 10 ideas changing the world right now - TIME magazine. http://content.time.com/time/specials/packages/article/0,28804,1884779_1.... Accessed 14 Aug 2020
-
- Pandya J (2019) Biobanking is changing the world. https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/ 2019/08/12/biobanking-is-changing-the-world/#31e7fa673792. Accessed 30 Nov 2020
-
- Mendy M, Caboux E, Lawlor RT, et al. Common minimum technical standards and protocols for biobanks dedicated to cancer research, IARC Techn. Lyon Cedex: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

