Serum CK-MB, COVID-19 severity and mortality: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression
- PMID: 34256241
- PMCID: PMC8260505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advms.2021.07.001
Serum CK-MB, COVID-19 severity and mortality: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression
Abstract
Objectives: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression of creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), a biomarker of myocardial injury, in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Web of Science and Scopus, for studies published between January 2020 and January 2021 that reported CK-MB, COVID-19 severity and mortality (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42021239657).
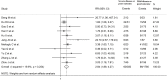
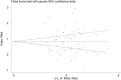
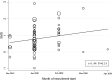
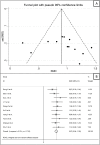
Results: Fifty-five studies in 11,791 COVID-19 patients were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled results showed that CK-MB concentrations were significantly higher in patients with high disease severity or non-survivor status than patients with low severity or survivor status (standardized mean difference, SMD, 0.81, 95% CI 0.61 to 1.01, p<0.001). The rate of patients with CK-MB values above the normal range was also significantly higher in the former than the latter (60/350 vs 98/1,780; RR = 2.84, 95%CI 1.89 to 4.27, p<0.001; I2 = 19.9, p = 0.254). Extreme between-study heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 93.4%, p<0.001). Sensitivity analysis, performed by sequentially removing each study and re-assessing the pooled estimates, showed that the magnitude and direction of the effect size was not modified (effect size range, 0.77 to 0.84). Begg's (p = 0.50) and Egger's (p = 0.86) t-tests did not show publication bias. In meta-regression analysis, the SMD was significantly and positively associated with the white blood count, aspartate aminotransferase, myoglobin, troponin, brain natriuretic peptide, lactate dehydrogenase, and D-dimer.
Conclusions: Higher CK-MB concentrations were significantly associated with severe disease and mortality in COVID-19 patients. This biomarker of myocardial injury might be useful for risk stratification in this group.
Keywords: COVID-19; Creatine kinase-MB; Creatine kinase-MB values Above the normal range; Disease severity; Mortality.
Copyright © 2021 Medical University of Bialystok. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Huang C., Soleimani J., Herasevich S., Pinevich Y., Pennington K.M., Dong Y., Pickering B.W., Barwise A.K. Clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19: a scoping review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96:183–202. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.10.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pijls B.G., Jolani S., Atherley A., Derckx R.T., Dijkstra J.I.R., Franssen G.H.L., Hendriks S., Richters A., Venemans-Jellema A., Zalpuri S., Zeegers M.P. Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: a meta-analysis of 59 studies. BMJ Open. 2021;11 doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044640. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paliogiannis P., Zinellu A., Scano V., Mulas G., De Riu G., Pascale R.M., Arru L.B., Carru C., Pirina P., Mangoni A.A., Fois A.G. Laboratory test alterations in patients with COVID-19 and non COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia: a preliminary report. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020;14:685–690. doi: 10.3855/jidc.12879. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao Y.D., Ding M., Dong X., Zhang J.J., Kursat Azkur A., Azkur D., Gan H., Sun Y.L., Fu W., Li W., Liang H.L., Cao Y.Y., Yan Q., Cao C., Gao H.Y., Bruggen M.C., van de Veen W., Sokolowska M., Akdis M., Akdis C.A. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: a review. Allergy. 2021;76:428–455. doi: 10.1111/all.14657. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

