Contribution of traditional Chinese medicine combined with conventional western medicine treatment for the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), current evidence with systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34256418
- PMCID: PMC8441775
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.7209
Contribution of traditional Chinese medicine combined with conventional western medicine treatment for the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), current evidence with systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
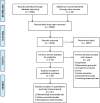
This study provides current evidence for efficacy and safety of treating COVID-19 with combined traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and conventional western medicine (CWM). Six databases were searched from January 1 to December 31, 2020. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), case-control studies (CCTs), and cohort studies on TCM or TCM combined with CWM treatment for COVID-19 were included. The quality of included RCTs was assessed by Cochrane risk of bias tool, and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess the quality of cohort studies and CCTs. Review Manager 5.4 software was used to perform meta-analysis. The quality of evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach. A total of 35 studies (3,808 patients) composing 19 RCTs and 16 observational studies were included. The results of meta-analysis revealed that comparing with CWM alone, integrated TCM and CWM had significant improvement in total effective rate, improvement rate of chest CT, the rate of disease progression, as well as improvement of fever, fatigue and cough. The overall quality of evidence was very low to moderate. In conclusion, TCM combined with CWM was a potential treatment option for increasing clinical effective rate, improving the clinical symptoms, and preventing disease progression in COVID-19 patients. High-quality clinical trials are required in the further.
Keywords: COVID-19; integrative medicine; meta-analysis; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there was no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Brendler, T. , Al‐Harrasi, A. , Bauer, R. , Gafner, S. , Hardy, M. L. , Heinrich, M. , … Williamson, E. M. (2020). Botanical drugs and supplements affecting the immune response in the time of COVID‐19: Implications for research and clinical practice. Phytotherapy Research, 35, 3013–3031. 10.1002/ptr.7008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen, L. , Chen, Y. G. , Cheng, Z. Q. , Liu, F. , Wu, J. H. , Xia, Y. , & Sheng, B. (2020). Retrospective analysis on clinical efficacy of Ganlu Xiaodu decoction combined with Western medicine in treatment of common COVID‐19 patients. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 26(19), 60–67. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20202011 - DOI
-
- Chen, L. , Liu, F. , Wu, J. H. , Song, H. Y. , Xia, J. S. , Sheng, B. , & Chen, Y. G. (2020). Clinical efficacy of Shufeng Jiedu capsule combined with western medicine in treatment of common COVID‐19 patients by retrospective analysis. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 36(16), 16–20. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20201628 - DOI
-
- Cheng, D. Z. , Wang, W. J. , Li, Y. , Wu, X. D. , Zhou, B. , & Song, Q. Y. (2020). Efficacy analysis on 51 cases of COVID‐19 treated with traditional Chinese medicine Lianhua Qingwen: A multi‐center retrospective study. Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 37(5), 509–516. 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2020.05.06 - DOI
-
- Ding, X. J. , Zhang, Y. , He, D. C. , Zhang, M. Y. , Tan, Y. J. , Yu, A. R. , … Liu, L. (2020). Clinical effect and mechanism of Qingfei Touxie Fuzheng recipe in the treatment of Novel Coronavirus pneumonia. Herald of Medicine, 39(5), 640–644. 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2020.05.012 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81870005/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 18KJA180003/Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD)
- KC20102/Project of Xuzhou Applied and Basic Research
- KC18009/Project of Xuzhou Applied and Basic Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

