Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis/pseudomonas
- PMID: 34257107
- PMCID: PMC8278921
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236887
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis/pseudomonas
Abstract
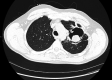
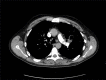
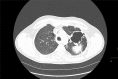
A 47-year-old Caucasian man on long-standing antifungal therapy for chronic necrotising aspergillosis and a history of recurrent pseudomonas pneumonias presented to the outpatient pulmonary clinic with dyspnoea and chest discomfort for 3 days. A CT angiography of the chest demonstrated angioinvasion from the previously noted left upper lobe cavitary lesion into the left main pulmonary artery, along with new consolidating lesions. Due to the high risk for massive haemoptysis, he was evaluated by thoracic surgery and underwent a successful left pneumonectomy. As invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is associated with high mortality, surgical intervention should always be considered, especially in those who develop extensive disease, despite being on aggressive antifungal therapy. Though minimally described in literature, invasive pulmonary pseudomonas also carries a high mortality risk. In our patient, cultures from the resected lung only demonstrated Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Keywords: TB and other respiratory infections; pneumonia (infectious disease).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Broaddus VC, Mason RJ, Ernst JD. Aspergillosis. Murray & Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine 2016:670–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
