Development of a municipality index of environmental pressure in Campania, Italy
- PMID: 34258027
- PMCID: PMC8256331
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2021-0055
Development of a municipality index of environmental pressure in Campania, Italy
Abstract
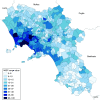
The Experimental Zooprophylactic Institute of Southern Italy (Istitituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale del Mezzogiorno, IZSM) is a public health institution operating within the Italian National Health Service. Over the past 5 years [IZSM] has promoted several research studies and interventions in an effort to tackle the 'Land of Fires' phenomenon, caused by the continued trafficking and uncontrolled incineration of waste that has affected some areas of Campania for decades. In this article, a mathematical model that generates a municipality index of environmental pressure is presented. The model was developed by a multidisciplinary team led by an environmental engineer and included researchers in the fields of veterinary and human medicine, biology and computer science. This model may serve as a geostratification tool useful for the design of human biomonitoring studies, although it may also be employed for strategic planning of remediation programs and public health interventions.
Keywords: Land of Fires; SPES trial; biomonitoring; environmental monitoring.
© 2021 Carlo Buonerba.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure Translation services were supplied by Translated S.r.l., funding of which was supported by Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale del Mezzogiorno. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed. No further writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Legambiente. Rapporto Ecomafia 2003. www.legambiente.it/sites/default/files/docs/Rapporto_Ecomafia_2003_00000...
-
- Costa S. La situazione rifiuti in Campania: dall’emergenza alla gestione ordinaria. http://cdca.it/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/41_60.pdf
-
- Cantoni R. The waste crisis in Campania, South Italy: a historical perspective on an epidemiological controversy. Endeavour 40(2), 102–113 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Senior K, Mazza A. Italian ‘triangle of death’ linked to waste crisis. Lancet Oncol. 5(9), 525–527 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Bianchi F, Comba P, Martuzzi M, Palombino R, Pizzuti R. Italian ‘triangle of death’. Lancet Oncol. 5(12), 710 (2004). - PubMed
-
•• The first study that hypothesized an increased risk of cancer-related death due to illegal waste trafficking.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
