Central Type II Glucocorticoid Receptor Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Glycogen Metabolic Enzyme and Glucoregulatory Neurotransmitter Marker Protein Expression in the Male Rat
- PMID: 34258390
- PMCID: PMC8274514
Central Type II Glucocorticoid Receptor Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Glycogen Metabolic Enzyme and Glucoregulatory Neurotransmitter Marker Protein Expression in the Male Rat
Abstract
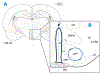
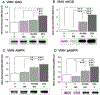
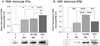
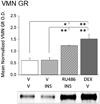
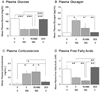
The ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMN) glucoregulatory neurotransmitters γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and nitric oxide (NO) signal adjustments in glycogen mobilization. Glucocorticoids control astrocyte glycogen metabolism in vitro. The classical (type II) glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is expressed in key brain structures that govern glucostasis, including the VMN. Current research addressed the hypothesis that forebrain GR regulation of VMN glycogen synthase (GS) and phosphorylase (GP) protein expression correlates with control of glucoregulatory transmission. Groups of male rats were pretreated by intracerebroventricular (icv) delivery of the GR antagonist RU486 or vehicle prior to insulin-induced hypoglycemia (IIH), or were pretreated icv with dexamethasone (DEX) or vehicle before subcutaneous insulin diluent injection. DEX increased VMN GS and norepinephrine-sensitive GP-muscle type (GPmm), but did not alter metabolic deficit-sensitive GP-brain type (GPbb) expression. RU486 enhanced GS and GPbb profiles during IIH. VMN astrocyte (MCT1) and neuronal (MCT2) monocarboxylate transporter profiles were up-regulated in euglycemic and hypoglycemic animals by DEX or RU486, respectively. Glutamate decarboxylase65/67 and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) proteins were both increased by DEX, yet RU486 augmented hypoglycemic nNOS expression patterns. Results show that GR exert divergent effects on VMN GS, MCT1/2, and nNOS proteins during eu- (stimulatory) versus hypoglycemia (inhibitory); these findings imply that up-regulated NO transmission may reflect, in part, augmented glucose incorporation into glycogen and/or increased tissue lactate requirements. Data also provide novel evidence for metabolic state-dependent GR regulation of VMN GPmm and GPbb profiles; thus, GABA signaling of metabolic stability may reflect, in part, stimulus-specific glycogen breakdown during eu- versus hypoglycemia.
Keywords: Dexamethasone; Glucocorticoid receptor; Glycogen phosphorylase; Nitric oxide synthase; RU486; Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest The authors have no interests to declare.
Figures

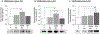
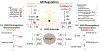
Similar articles
-
Glycogen phosphorylase isoenzyme GPbb versus GPmm regulation of ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus glucoregulatory neurotransmitter and counter-regulatory hormone profiles during hypoglycemia: Role of L-lactate and octadecaneuropeptide.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2023 Sep;126:103863. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2023.103863. Epub 2023 May 31. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37268282 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen Phosphorylase Isoform Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Gluco-Regulatory Neuron 5'-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Transmitter Marker Protein Expression.ASN Neuro. 2021 Jan-Dec;13:17590914211035020. doi: 10.1177/17590914211035020. ASN Neuro. 2021. PMID: 34596459 Free PMC article.
-
Hindbrain catecholamine regulation of ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus glycogen metabolism during acute versus recurring insulin-induced hypoglycemia in male versus female rat.Endocr Metab Sci. 2021 Jun 30;3:100087. doi: 10.1016/j.endmts.2021.100087. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Endocr Metab Sci. 2021. PMID: 33997825 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Astrocyte Glycogen Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 13;22(2):759. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020759. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33451134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Norepinephrine Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Metabolic-Sensory Neuron 5'-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activity: Impact of Estradiol.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 16;21(6):2013. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062013. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32188013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Dimorphic Glucocorticoid Receptor Regulation of Hypothalamic Primary Astrocyte Glycogen Metabolism: Interaction with Norepinephrine.Neuroglia. 2022 Dec;3(4):144-157. doi: 10.3390/neuroglia3040010. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Neuroglia. 2022. PMID: 36685006 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
