Hawthorn pectin: Extraction, function and utilization
- PMID: 34258587
- PMCID: PMC8253901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.06.002
Hawthorn pectin: Extraction, function and utilization
Abstract
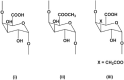
Pectin has been widely used as emulsifiers, gelling agents, glazing agents, stabilizers, and thickeners in food products. Hawthorn pectin has a higher viscosity than other foods-derived pectin such as lemon and apple pectin. It is also reported as a multifunctional fruit substance, which reduces the risk of hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia. Therefore, hawthorn pectin is a potential resource for the development of new drugs, functional foods, and health-care products. This review symmetrically summarized the extraction methods, physiological characteristics, functional properties, and processing technologies of hawthorn pectin. It laid a foundation for the further research of hawthorn pectin and promoted the diversified utilization of hawthorn.
Keywords: Extraction; Function; Hawthorn pectin; Modification; Processing.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Adetunji Lanrewaju Ridwan, Adekunle Ademola, Orsat Valérie, Raghavan Vijaya. Advances in the pectin production process using novel extraction techniques: a review. Food Hydrocolloids. 2017;62:239–250.
-
- Bergman M., Djaldetti M., Salman H., Bessler H. Effect of citrus pectin on malignant cell proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010;64:44–47. - PubMed
-
- Bray George A., Paeratakul Sahasporn, Popkin Barry M. Dietary fat and obesity: a review of animal, clinical and epidemiological studies. Physiol. Behav. 2004;83:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee Iain A. The physiological roles of dietary fibre. Food Hydrocolloids. 2011;25:238–250.
-
- Cárdenas Adriana, Goycoolea Francisco M., Rinaudo Marguerite. On the gelling behaviour of ‘nopal’ (Opuntia ficus indica) low methoxyl pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008;73:212–222.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

