Biodistribution of Exosomes and Engineering Strategies for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Exosomes
- PMID: 34260047
- PMCID: PMC8325750
- DOI: 10.1007/s13770-021-00361-0
Biodistribution of Exosomes and Engineering Strategies for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Exosomes
Abstract
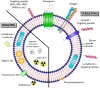
Exosomes are cell-secreted nano-sized vesicles which deliver diverse biological molecules for intercellular communication. Due to their therapeutic potential, exosomes have been engineered in numerous ways for efficient delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients to various target organs, tissues, and cells. In vivo administered exosomes are normally delivered to the liver, spleen, kidney, lung, and gastrointestinal tract and show rapid clearance from the blood circulation after systemic injection. The biodistribution and pharmacokinetics (PK) of exosomes can be modulated by engineering various factors such as cellular origin and membrane protein composition of exosomes. Recent advances accentuate the potential of targeted delivery of engineered exosomes even to the most challenging organs including the central nervous system. Major breakthroughs have been made related to various imaging techniques for monitoring in vivo biodistribution and PK of exosomes, as well as exosomal surface engineering technologies for inducing targetability. For inducing targeted delivery, therapeutic exosomes can be engineered to express various targeting moieties via direct modification methods such as chemically modifying exosomal surfaces with covalent/non-covalent bonds, or via indirect modification methods by genetically engineering exosome-producing cells. In this review, we describe the current knowledge of biodistribution and PK of exosomes, factors determining the targetability and organotropism of exosomes, and imaging technologies to monitor in vivo administered exosomes. In addition, we highlight recent advances in strategies for inducing targeted delivery of exosomes to specific organs and cells.
Keywords: Biodistribution; Exosome; Pharmacokinetics; Targeted delivery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CC is the founder and shareholder, and JY, HC, HY are minor shareholders of ILIAS Biologics Inc. The authors have no additional financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surface functionalization of exosomes for target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking: Strategies and significance.J Control Release. 2020 Oct 10;326:599-614. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.042. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32730952 Review.
-
Biological characteristics of exosomes and genetically engineered exosomes for the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.J Drug Target. 2020 Feb;28(2):129-141. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2019.1641508. Epub 2019 Aug 12. J Drug Target. 2020. PMID: 31280623 Review.
-
Targeted Delivery of Exosomes Armed with Anti-Cancer Therapeutics.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/membranes12010085. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapeutic delivery using engineered exosomes and its applications in cardiovascular diseases.Gene. 2016 Jan 10;575(2 Pt 2):377-384. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.067. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26341056 Review.
-
Challenges and future scope of exosomes in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):4873-4893. doi: 10.1113/JP282053. Epub 2022 Dec 3. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36398654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time monitoring of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) by in vivo flow cytometry.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Oct;13(10):e70003. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70003. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 39441010 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances of Engineered Exosomes as Drug Delivery Carrier.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 9;8(46):43374-43387. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04479. eCollection 2023 Nov 21. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38027310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Dichloroacetate: Targeting Metabolic Disorders in Nervous System Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 12;18:7559-7581. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S439728. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38106446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Imaging Biomarkers in the Management of Chronic Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13038. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113038. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Exosomes as the Next-Generation Bio-Shuttles: The Next Biggest Approach against Th17 Cell Catastrophe.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7647. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087647. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fradelizi D. Cytokines: soluble factors in intercellular communication. Med Trop (Mars) 1998;58:427–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
