Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 34261330
- PMCID: PMC8384252
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315754
Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
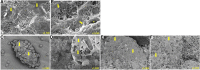
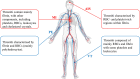
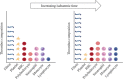
Thrombosis is a major complication of cardiovascular disease, leading to myocardial infarction, acute ischemic stroke, or venous thromboembolism. Thrombosis occurs when a thrombus forms inside blood vessels disrupting blood flow. Developments in thrombectomy to remove thrombi from vessels have provided new opportunities to study thrombus composition which may help to understand mechanisms of disease and underpin improvements in treatments. We aimed to review thrombus compositions, roles of components in thrombus formation and stability, and methods to investigate thrombi. Also, we summarize studies on thrombus structure obtained from cardiovascular patients and animal models. Thrombi are composed of fibrin, red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes, and neutrophil extracellular traps. These components have been analyzed by several techniques, including scanning electron microscopy, laser scanning confocal microscopy, histochemistry, and immunohistochemistry; however, each technique has advantages and limitations. Thrombi are heterogenous in composition, but overall, thrombi obtained from myocardial infarction are composed of mainly fibrin and other components, including platelets, red blood cells, leukocytes, and cholesterol crystals. Thrombi from patients with acute ischemic stroke are characterized by red blood cell- and platelet-rich regions. Thrombi from patients with venous thromboembolism contain mainly red blood cells and fibrin with some platelets and leukocytes. Thrombus composition from patients with myocardial infarction is influenced by ischemic time. Animal thrombosis models are crucial to gain further mechanistic information about thrombosis and thrombus structure, with thrombi being similar in composition compared with those from patients. Further studies on thrombus composition and function are key to improve treatment and clinical outcome of thrombosis.
Keywords: blood vessels; cardiovascular diseases; myocardial infarction; thrombectomy; thrombosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histologic features of acute thrombi retrieved from stroke patients during mechanical reperfusion therapy.Int J Stroke. 2016 Dec;11(9):1036-1044. doi: 10.1177/1747493016641965. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Int J Stroke. 2016. PMID: 27056965
-
Acute ischemic stroke thrombi have an outer shell that impairs fibrinolysis.Neurology. 2019 Oct 29;93(18):e1686-e1698. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008395. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 31541014 Free PMC article.
-
Association between thrombus composition and first-pass recanalization after thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke.J Thromb Haemost. 2024 Sep;22(9):2555-2561. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.05.034. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38897388
-
Thrombus Composition and Efficacy of Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke.Stroke. 2021 Mar;52(3):1131-1142. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032810. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33563020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombus aspiration therapy and coronary thrombus components in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013;20(6):524-37. doi: 10.5551/jat.17608. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013. PMID: 23629150 Review.
Cited by
-
Factor V Leiden (R506Q), Prothrombin G20210A, and MTHFR C677T Variants and Thrombophilia in Qatar Biobank Participants: A Case Control Study.Pathophysiology. 2024 Oct 21;31(4):608-620. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31040044. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39449526 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products in drug discovery and development: Synthesis and medicinal perspective of leonurine.Front Chem. 2022 Oct 17;10:1036329. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1036329. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36324522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Therapeutic Efficacy and Adverse Reactions among Various Thrombolytic Agents.Toxics. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):458. doi: 10.3390/toxics12070458. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39058110 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and Molecular Docking Studies of Pleurospermum candollei: An Insight into Potential for Natural Products Development.Molecules. 2022 Jun 26;27(13):4113. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134113. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807359 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombus-Targeting Polymeric Nanocarriers and Their Biomedical Applications in Thrombolytic Therapy.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 30;12:763085. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.763085. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34916956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Undas A, Ariëns RA. Fibrin clot structure and function: a role in the pathophysiology of arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:e88–e99. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.230631 - PubMed
-
- Weisel JW. The mechanical properties of fibrin for basic scientists and clinicians. Biophys Chem. 2004;112:267–276. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2004.07.029 - PubMed
-
- Collet JP, Park D, Lesty C, Soria J, Soria C, Montalescot G, Weisel JW. Influence of fibrin network conformation and fibrin fiber diameter on fibrinolysis speed: dynamic and structural approaches by confocal microscopy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1354–1361. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.5.1354 - PubMed

