Expression of Transcription Factor CREM in Human Tissues
- PMID: 34261344
- PMCID: PMC8329441
- DOI: 10.1369/00221554211032008
Expression of Transcription Factor CREM in Human Tissues
Abstract
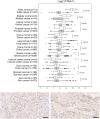
Cyclic AMP element modulator (CREM) is a transcription factor best known for its intricate involvement in spermatogenesis. The CREM gene encodes for multiple protein isoforms, which can enhance or repress transcription of target genes. Recent studies have identified fusion genes, with CREM as a partner gene in many neoplastic diseases. EWSR1-CREM fusion genes have been found in several mesenchymal tumors and in salivary gland carcinoma. These genes encode fusion proteins that include the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of CREM. We used a transcriptomic approach and immunohistochemistry to study the expression of CREM isoforms that include DNA-binding domains across human tissues. We found that CREM protein is widely expressed in almost all normal human tissues. A transcriptomic analysis of normal tissues and cancer showed that transcription of CREM can be altered in tumors, suggesting that also wild-type CREM may be involved in cancer biology. The wide expression of CREM protein in normal human tissues and cancer may limit the utility of immunohistochemistry for identification of tumors with CREM fusions.
Keywords: CREB; CREM; ICER; cancer; cyclic AMP element modulator; fusion gene; immunohistochemistry; normal tissue; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Brindle PK, Montminy MR. The CREB family of transcription activators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992;2(2):199–204. - PubMed
-
- Sassone-Corsi P. Coupling gene expression to cAMP signalling: role of CREB and CREM. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;30(1):27–38. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Jin W, Liu X, Fu H, Gong P, Xu J, Cui G, Ni Y, Ke K, Gao Z, Gao Y. Cyclic AMP response element modulator-1 (CREM-1) involves in neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;47(2):357–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

