Integrative Profiling of T790M-Negative EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Reveals Pervasive Lineage Transition and Therapeutic Opportunities
- PMID: 34261696
- PMCID: PMC9401458
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4607
Integrative Profiling of T790M-Negative EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Reveals Pervasive Lineage Transition and Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
Purpose: Despite the established role of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in EGFR-mutated NSCLC, drug resistance inevitably ensues, with a paucity of treatment options especially in EGFR T790M-negative resistance.
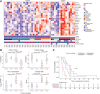
Experimental design: We performed whole-exome and transcriptome analysis of 59 patients with first- and second-generation EGFR TKI-resistant metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC to characterize and compare molecular alterations mediating resistance in T790M-positive (T790M+) and -negative (T790M-) disease.
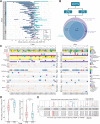
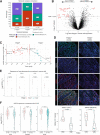
Results: Transcriptomic analysis revealed ubiquitous loss of adenocarcinoma lineage gene expression in T790M- tumors, orthogonally validated using multiplex IHC. There was enrichment of genomic features such as TP53 alterations, 3q chromosomal amplifications, whole-genome doubling and nonaging mutational signatures in T790M- tumors. Almost half of resistant tumors were further classified as immunehot, with clinical outcomes conditional on immune cell-infiltration state and T790M status. Finally, using a Bayesian statistical approach, we explored how T790M- and T790M+ disease might be predicted using comprehensive genomic and transcriptomic profiles of treatment-naïve patients.
Conclusions: Our results illustrate the interplay between genetic alterations, cell lineage plasticity, and immune microenvironment in shaping divergent TKI resistance and outcome trajectories in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling may facilitate the design of bespoke therapeutic approaches tailored to a tumor's adaptive potential.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Thongprasert S, Yang C-H, Chu D-T, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2009;361:947–57. - PubMed
-
- Park K, Tan E-H, O'Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer M, Mok T, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non–small cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): a phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:577–89. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non–small cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Soria J-C, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;378:113–25. - PubMed
-
- Noronha V, Patil VM, Joshi A, Menon N, Chougule A, Mahajan A, et al. Gefitinib versus gefitinib plus pemetrexed and carboplatin chemotherapy in EGFR-mutated lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2020;38:124–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

