A novel dephosphorylation targeting chimera selectively promoting tau removal in tauopathies
- PMID: 34262014
- PMCID: PMC8280143
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00669-2
A novel dephosphorylation targeting chimera selectively promoting tau removal in tauopathies
Abstract
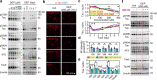
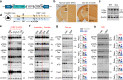
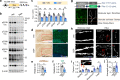
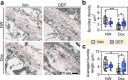
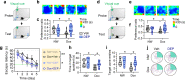
Intraneuronal accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau is a hallmark pathology shown in over twenty neurodegenerative disorders, collectively termed as tauopathies, including the most common Alzheimer's disease (AD). Therefore, selectively removing or reducing hyperphosphorylated tau is promising for therapies of AD and other tauopathies. Here, we designed and synthesized a novel DEPhosphorylation TArgeting Chimera (DEPTAC) to specifically facilitate the binding of tau to Bα-subunit-containing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A-Bα), the most active tau phosphatase in the brain. The DEPTAC exhibited high efficiency in dephosphorylating tau at multiple AD-associated sites and preventing tau accumulation both in vitro and in vivo. Further studies revealed that DEPTAC significantly improved microtubule assembly, neurite plasticity, and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory in transgenic mice with inducible overexpression of truncated and neurotoxic human tau N368. Our data provide a strategy for selective removal of the hyperphosphorylated tau, which sheds new light for the targeted therapy of AD and related-tauopathies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J-Z.W. and J.Z. have filed for a patent related to this work (CN109824787A). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

