rasterdiv-An Information Theory tailored R package for measuring ecosystem heterogeneity from space: To the origin and back
- PMID: 34262682
- PMCID: PMC8252722
- DOI: 10.1111/2041-210X.13583
rasterdiv-An Information Theory tailored R package for measuring ecosystem heterogeneity from space: To the origin and back
Abstract
Ecosystem heterogeneity has been widely recognized as a key ecological indicator of several ecological functions, diversity patterns and change, metapopulation dynamics, population connectivity or gene flow.In this paper, we present a new R package-rasterdiv-to calculate heterogeneity indices based on remotely sensed data. We also provide an ecological application at the landscape scale and demonstrate its power in revealing potentially hidden heterogeneity patterns.The rasterdiv package allows calculating multiple indices, robustly rooted in Information Theory, and based on reproducible open-source algorithms.
Keywords: biodiversity; ecological informatics; modelling; remote sensing; satellite imagery.
© 2021 The Authors. Methods in Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Ecological Society.
Figures


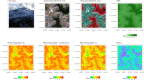
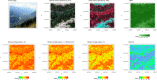
References
-
- August, P. V. (1983). The role of habitat complexity and heterogeneity in structuring tropical mammal communities. Ecology, 64, 1495–1507.
-
- Blonder, B. (2018). Hypervolume concepts in niche‐ and trait‐based ecology. Ecography, 41, 1441–1455. 10.1111/ecog.03187 - DOI
-
- Boltzmann, L. E. (1872). Weitere studien über das waärmegleichgewicht unter gasmolekälen. S K Akad Wiss Wein, 66, 275–370.
-
- Da Re, D. , De Clercq, E. M. , Tordoni, E. , Madder, M. , Rousseau, R. , & Vanwambeke, S. O. (2019). Looking for ticks from space: Using remotely sensed spectral diversity to assess Amblyomma and Hyalomma tick abundance. Remote Sensing, 11, 770.
-
- Doxa, A. , & Prastacos, P. (2020). Using Rao's quadratic entropy to define environmental heterogeneity priority areas in the European Mediterranean biome. Biological Conservation, 241, 108366.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
