Targeting CD22 for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies
- PMID: 34262884
- PMCID: PMC8275043
- DOI: 10.2147/ITT.S288546
Targeting CD22 for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies
Abstract
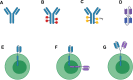
Immunotherapeutic agents play an increasingly important role in the treatment of B-cell malignancies. CD19 and CD20 are common targets for lymphoid malignancies, though patients who relapse have few therapeutic options remaining. CD22 is a cell surface sialoglycoprotein uniquely present on B-cells and regulates B-cell function and proliferation. Thus, it is an appealing therapeutic target for autoimmune disorders and B-cell malignancies. A variety of therapies targeting CD22 have been developed, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, radioimmunoconjugates, chimeric antigen receptor T cells, and bispecific antibodies. Here, we review the biology of CD22 and key therapies targeting CD22 in lymphoid malignancies.
Keywords: CD22; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; bispecific antibody; chimeric antigen receptor; epratuzumab; inotuzumab ozogamicin; lymphoma.
© 2021 Shah and Sokol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Morrison VA, Hong F, Habermann TM, et al. R-CHOP Versus (vs) CHOP Followed by Maintenance Rituximab (MR) Vs Observation In Older Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Patients (pts): long-Term Follow-up of Intergroup E4494/C9793. Blood. 2010;116:589. doi:10.1182/blood.V116.21.589.589 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

