Gastrointestinal Histoplasmosis Mimicking Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 34262987
- PMCID: PMC8274358
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab249
Gastrointestinal Histoplasmosis Mimicking Crohn's Disease
Abstract
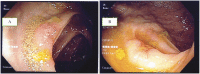
Disseminated histoplasmosis is a life-threatening disease usually seen in immunocompromised patients living in endemic areas. We present an apparently immunocompetent patient with gastrointestinal histoplasmosis who was initially diagnosed with biopsy-proven Crohn's disease. Following discontinuation of anti-inflammatory drugs and institution of antifungal therapy, his gastrointestinal illness completely improved. Specific fungal staining should be routinely included in histopathologic assessment of tissue specimens diagnosed as Crohn's disease.
Keywords: alcoholism; gastrointestinal histoplasmosis; inflammatory bowel disease.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures


References
-
- Assi MA, Sandid MS, Baddour LM, et al. . Systemic histoplasmosis: a 15-year retrospective institutional review of 111 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007; 86:162–9. - PubMed
-
- Kahi CJ, Wheat LJ, Allen SD, Sarosi GA. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2005; 100:220–31. - PubMed
-
- Romano RC, Soape MM, Thirumala S, Ghandour E. Disseminated histoplasmosis mimicking metastatic disease of the colon and omentum: report of a case and literature review. Arab J Gastroenterol 2015; 16:66–8. - PubMed

