Impact of an institutional grant award on early career investigator applicants and peer reviewers
- PMID: 34263104
- PMCID: PMC8268663
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12555
Impact of an institutional grant award on early career investigator applicants and peer reviewers
Abstract
Background: Obtaining research funding support is integral to a successful career in science. Training and practice in grant writing, as well as engagement in peer review of grant applications may help lead to successful research funding. However, there is little evidence on the impact of institutional programs on the career development of early career investigators (ECIs).
Objectives: Understand the impact of participation in an institutional research award program on the career development of ECIs.
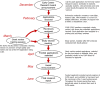
Methods: The Cardiovascular Research Institute of Vermont established an Early Career Research (ECR) award program in 2018. ECIs who participated as applicants or reviewers in the first 3 years of the program (2018-2020) were surveyed to understand the impact of the ECR award program on their grant writing and professional development.
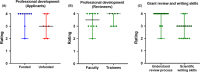
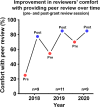
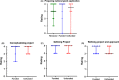
Results: Ninety-four percent of 17 applicants and 90% of 19 reviewers completed the survey. Ninety-two percent of funded and 75% of unfunded applicants, and 87% of reviewers reported that the program was beneficial to their professional development. Similarly, 85% of funded applicants, 75% of unfunded applicants, and 80% of reviewers reported improvement in their grant-writing skills. All respondents reported they would recommend the ECR award program to their peers.
Conclusions: This single-institution ECR award program had a positive impact on ECI's professional development and grant-writing skills and may lead to further extramural funding opportunities.
Keywords: award; institute; peer review; surveys and questionnaires; writing.
© 2021 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of a Career Development Award (Pre-K) Mock Review Program for Postdoctoral Fellows and Early-Career Faculty.Acad Med. 2023 Nov 1;98(11):1313-1318. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000005293. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Acad Med. 2023. PMID: 37289813 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences in grant and personnel award funding rates at the Canadian Institutes of Health Research based on research content area: A retrospective analysis.PLoS Med. 2019 Oct 15;16(10):e1002935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002935. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31613898 Free PMC article.
-
Launching IDeA state early career clinician-scientists with mentored just-in-time grant-writing support.J Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Sep 4;7(1):e197. doi: 10.1017/cts.2023.625. eCollection 2023. J Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37771413 Free PMC article.
-
How well does early-career investigators' cardiovascular outcomes research training align with funded outcomes research?Am Heart J. 2018 Feb;196:163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Am Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29421009 Review.
-
A practical guide to writing a competitive K award application.Surgery. 2021 Nov;170(5):1411-1417. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2021.05.017. Epub 2021 Jun 13. Surgery. 2021. PMID: 34134898 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Initiative Supporting Excellence at the University of Cincinnati (RISE-UC): A Program to Develop and Support Research-Active Faculty Members.Acad Med. 2023 Oct 1;98(10):1120-1130. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000005270. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Acad Med. 2023. PMID: 37200479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foundation NS . Biological Sciences (BIO) Funding Rates 2020. https://www.nsf.gov/funding/funding‐rates.jsp?org=BIO. 21 Oct, 2020.
-
- Association AH . Success Rates 2020. https://professional.heart.org/en/research‐programs/aha‐research‐accompl.... 6 Dec, 2020.
-
- Health NIo . Funding Facts 2018 updated June 30, 2018. https://report.nih.gov/fundingfacts/fundingfacts.aspx. 21 Oct, 2020.
-
- Freeman R, Weinstein E, Marincola E, Rosenbaum J, Solomon F. Competition and Careers in Biosciences. Science. 2001;294(5550):2293–2294. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

