Normalization of left ventricular filling pressure after cardiac surgery for the Loeffler's endocarditis: a case report
- PMID: 34263118
- PMCID: PMC8274654
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytab189
Normalization of left ventricular filling pressure after cardiac surgery for the Loeffler's endocarditis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Loeffler endocarditis is a rare restrictive cardiomyopathy, characterized by hypereosinophilia and fibrous thickening of the endocardium causing progressive onset of heart failure and appearance of thrombi on the walls of the heart chambers.
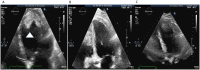
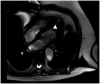
Case summary: A 72-year-old man known for hypertension and dyslipidaemia consults for progressive dyspnoea up to New York Heart Association (NYHA) Classes 2-3 over 3 weeks. The biological balance sheet shows a high eosinophil level and an echocardiography shows a mild echodensity fixed to the left apex. After exclusion of a secondary cause of hypereosinophilia, diagnosis of endomyocardial fibrosis in the context of a hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is therefore retained. The patient's clinical presentation with cardiac involvement leads us to start a treatment with corticosteroids. The patient is then regularly followed every 6 months with an initially stable course without complications. Two years later, he develops progressive signs of heart failure. Transthoracic echocardiography shows a left ventricular (LV) dilatation with a normal ejection fraction, but decreased volume due to a large echodense mass in the apex, and moderate aortic regurgitation caused by myocardial infiltration. In view of this rapid evolution, resection of the LV mass with concomitant aortic valve replacement is performed. Pathology confirms eosinophilic infiltration. The clinical course is very good with a patient who remains stable with dyspnoea NYHA Classes 1-2, and echocardiography at 1 year shows a normalization of LV filling pressure.
Discussion: HES represents a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by overproduction of eosinophils. One of the major causes of mortality is associated cardiac involvement. Endocardial fibrosis and mural thrombosis are frequent cardiac findings. Echocardiography plays a crucial role in initial diagnosis of endomyocardial fibrosis, and for regular follow-up in order to adapt medical treatment and monitor haemodynamic evolution of the restrictive physiology and of valvular damage caused by the disease's evolution. This case also shows that surgery can normalize filling pressure and allow a clear improvement on the clinical condition even at the terminal fibrotic state.
Keywords: Case report; Filling pressure; Hypereosinophilia; LV mass; Loeffler endocarditis; Restrictive cardiomyopathy.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Loeffler's endocarditis in a patient with a new diagnosed Churg-Strauss syndrome (CSS): A case report.Caspian J Intern Med. 2021 Winter;12(1):107-110. doi: 10.22088/cjim.12.1.107. Caspian J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33680407 Free PMC article.
-
Severe mitral regurgitation caused by eosinophilic endocarditis.J Cardiol Cases. 2014 Jul 7;10(3):108-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2014.05.012. eCollection 2014 Sep. J Cardiol Cases. 2014. PMID: 30546520 Free PMC article.
-
Loeffler endocarditis as a rare cause of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A case report and review of literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Mar;97(11):e0079. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010079. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29538200 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Early-Stage Loeffler's Endocarditis with Isolated Right Ventricular Involvement: Management, Long-Term Follow-Up, and Review of Literature.Echocardiography. 2016 Sep;33(9):1422-7. doi: 10.1111/echo.13264. Epub 2016 May 13. Echocardiography. 2016. PMID: 27172873 Review.
References
-
- Cogan E, Roufosse F.. Clinical management of the hypereosinophilic syndromes. Expert Rev Hematol 2012;5:275–290. - PubMed
-
- Podjasek HC, Butterfield JH.. Mortality in hypereosinophilic syndrome: 19 years of experience at Mayo Clinic with a review of the literature. Leuk Res 2013;37:392–395. - PubMed
-
- Pardanani A, Lasho T, Wassie E, Finke C, Zblewski D, Hanson CA. et al. Predictors of survival in WHO-defined hypereosinophilic syndrome and idiopathic hypereosinophilia and the role of next-generation sequencing. Leukemia 2016;30:1924–1926. - PubMed
-
- Weller PF, Bubley GJ.. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood 1994;83:2759. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
