Prognostic value of shock index in patients admitted with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the ARIC study community surveillance
- PMID: 34263294
- PMCID: PMC8557437
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuab050
Prognostic value of shock index in patients admitted with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the ARIC study community surveillance
Abstract
Aims: Shock index (SI), defined as the ratio of heart rate (HR) to systolic blood pressure (SBP), is easily obtained and predictive of mortality in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. However, large-scale evaluations of SI in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are lacking.
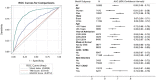
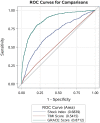
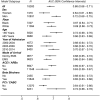
Methods and results: Hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction were sampled from four US areas by the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study and classified by physician review. Shock index was derived from the HR and SBP at first presentation and considered high when ≥0.7. From 2000 to 2014, 18 301 weighted hospitalizations for NSTEMI were sampled and had vitals successfully obtained. Of these, 5753 (31%) had high SI (≥0.7). Patients with high SI were more often female (46% vs. 39%) and had more prevalent chronic kidney disease (40% vs. 32%). TIMI (Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction) risk scores were similar between the groups (4.3 vs. 4.2), but GRACE (Global Registry of Acute Coronary Syndrome) score was higher with high SI (140 vs. 118). Angiography, revascularization, and guideline-directed medications were less often administered to patients with high SI, and the 28-day mortality was higher (13% vs. 5%). Prediction of 28-day mortality by SI as a continuous measurement [area under the curve (AUC): 0.68] was intermediate to that of the GRACE score (AUC: 0.87) and the TIMI score (AUC: 0.54). After adjustments, patients with high SI had twice the odds of 28-day mortality (odds ratio = 2.02; 95% confidence interval: 1.46-2.80).
Conclusion: The SI is easily obtainable, performs moderately well as a predictor of short-term mortality in patients hospitalized with NSTEMI, and may be useful for risk stratification in emergency settings.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; Epidemiology; Mortality; Risk score; NSTEMI.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Yussof SJ, Zakaria MI, Mohamed FL, Bujang MA, Lakshmanan S, Asaari AH.. Value of shock index in prognosticating the short-term outcome of death for patients presenting with severe sepsis and septic shock in the emergency department. Med J Malaysia 2012;67:406–411. - PubMed
-
- Rousseaux J, Grandbastien B, Dorkenoo A, Lampin ME, Leteurtre S, Leclerc F.. Prognostic value of shock index in children with septic shock. Pediatr Emerg Care 2013;29:1055–1059. - PubMed
-
- Sankaran P, Kamath AV, Tariq SM, Ruffell H, Smith AC, Prentice P, Subramanian DN, Musonda P, Myint PK.. Are shock index and adjusted shock index useful in predicting mortality and length of stay in community-acquired pneumonia? Eur J Intern Med 2011;22:282–285. - PubMed
-
- Myint PK, Bhaniani A, Bradshaw SM, Alobeidi F, Tariq SM.. Usefulness of shock index and adjusted shock index in the severity assessment of community-acquired pneumonia. Respiration 2009;77:468–469. - PubMed
-
- Toosi MS, Merlino JD, Leeper KV.. Prognostic value of the shock index along with transthoracic echocardiography in risk stratification of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 2008;101:700–705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201700001I/HH/HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

