Regulatory variants in TCF7L2 are associated with thoracic aortic aneurysm
- PMID: 34265237
- PMCID: PMC8456156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.06.016
Regulatory variants in TCF7L2 are associated with thoracic aortic aneurysm
Abstract
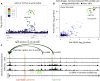
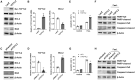
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) is characterized by dilation of the aortic root or ascending/descending aorta. TAA is a heritable disease that can be potentially life threatening. While 10%-20% of TAA cases are caused by rare, pathogenic variants in single genes, the origin of the majority of TAA cases remains unknown. A previous study implicated common variants in FBN1 with TAA disease risk. Here, we report a genome-wide scan of 1,351 TAA-affected individuals and 18,295 control individuals from the Cardiovascular Health Improvement Project and Michigan Genomics Initiative at the University of Michigan. We identified a genome-wide significant association with TAA for variants within the third intron of TCF7L2 following replication with meta-analysis of four additional independent cohorts. Common variants in this locus are the strongest known genetic risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Although evidence indicates the presence of different causal variants for TAA and type 2 diabetes at this locus, we observed an opposite direction of effect. The genetic association for TAA colocalizes with an aortic eQTL of TCF7L2, suggesting a functional relationship. These analyses predict an association of higher expression of TCF7L2 with TAA disease risk. In vitro, we show that upregulation of TCF7L2 is associated with BCL2 repression promoting vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis, a key driver of TAA disease.
Keywords: GWAS; TCF7L2; VSMC; apoptosis; regulatory variant; thoracic aortic aneurysm.
Copyright © 2021 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The spouse of C.J.W. is an employee of Regeneron. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hiratzka L.F., Bakris G.L., Beckman J.A., Bersin R.M., Carr V.F., Casey D.E., Jr., Eagle K.A., Hermann L.K., Isselbacher E.M., Kazerooni E.A. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with Thoracic Aortic Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation. 2010;121:e266–e369. - PubMed
-
- Dietz H.C., Cutting G.R., Pyeritz R.E., Maslen C.L., Sakai L.Y., Corson G.M., Puffenberger E.G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E.J., Curristin S.M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991;352:337–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 HG010464/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151776/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 CX001780/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- K08 HL130614/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL137214/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147527/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122664/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003362/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

