High risk groups for severe COVID-19 in a whole of population cohort in Australia
- PMID: 34266396
- PMCID: PMC8282405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06378-z
High risk groups for severe COVID-19 in a whole of population cohort in Australia
Abstract
Background: Increasing age is the strongest known risk factor for severe COVID-19 disease but information on other factors is more limited.
Methods: All cases of COVID-19 diagnosed from January-October 2020 in New South Wales Australia were followed for COVID-19-related hospitalisations, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and deaths through record linkage. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) for severe COVID-19 disease, measured by hospitalisation or death, or very severe COVID-19, measured by ICU admission or death according to age, sex, socioeconomic status and co-morbidities were estimated.
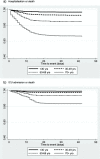
Results: Of 4054 confirmed cases, 468 (11.5%) were classified as having severe COVID-19 and 190 (4.7%) as having very severe disease. After adjusting for sex, socioeconomic status and comorbidities, increasing age led to the greatest risk of very severe disease. Compared to those 30-39 years, the aHR for ICU or death from COVID-19 was 4.45 in those 70-79 years; 8.43 in those 80-89 years; 16.19 in those 90+ years. After age, relative risks for very severe disease associated with other factors were more moderate: males vs females aHR 1.40 (95%CI 1.04-1.88); immunosuppressive conditions vs none aHR 2.20 (1.35-3.57); diabetes vs none aHR 1.88 (1.33-2.67); chronic lung disease vs none aHR 1.68 (1.18-2.38); obesity vs not obese aHR 1.52 (1.05-2.21). More comorbidities was associated with significantly greater risk; comparing those with 3+ comorbidities to those with none, aHR 5.34 (3.15-9.04).
Conclusions: In a setting with high COVID-19 case ascertainment and almost complete case follow-up, we found the risk of very severe disease varies by age, sex and presence of comorbidities. This variation should be considered in targeting prevention strategies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests as defined by BMC, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Dorjee K, Kim H, Bonomo E, Dolma R. Prevalence and predictors of death and severe disease in patients hospitalized due to COVID-19: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of 77 studies and 38,000 patients. PLoS One. 2020;15(12):e0243191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, Curtis HJ, Mehrkar A, Evans D, Inglesby P, Cockburn J, McDonald HI, MacKenna B, Tomlinson L, Douglas IJ, Rentsch CT, Mathur R, Wong AYS, Grieve R, Harrison D, Forbes H, Schultze A, Croker R, Parry J, Hester F, Harper S, Perera R, Evans SJW, Smeeth L, Goldacre B. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020;584(7821):430–436. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

