The Taxus genome provides insights into paclitaxel biosynthesis
- PMID: 34267359
- PMCID: PMC8367818
- DOI: 10.1038/s41477-021-00963-5
The Taxus genome provides insights into paclitaxel biosynthesis
Abstract
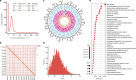
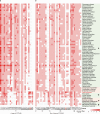
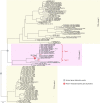
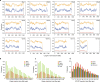
The ancient gymnosperm genus Taxus is the exclusive source of the anticancer drug paclitaxel, yet no reference genome sequences are available for comprehensively elucidating the paclitaxel biosynthesis pathway. We have completed a chromosome-level genome of Taxus chinensis var. mairei with a total length of 10.23 gigabases. Taxus shared an ancestral whole-genome duplication with the coniferophyte lineage and underwent distinct transposon evolution. We discovered a unique physical and functional grouping of CYP725As (cytochrome P450) in the Taxus genome for paclitaxel biosynthesis. We also identified a gene cluster for taxadiene biosynthesis, which was formed mainly by gene duplications. This study will facilitate the elucidation of paclitaxel biosynthesis and unleash the biotechnological potential of Taxus.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Comment in
-
Reference-grade Taxus genome unleashes its pharmacological potential.Trends Plant Sci. 2022 Jan;27(1):10-12. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.10.010. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Trends Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 34772612
References
-
- Christenhusz M, et al. A new classification and linear sequence of extant gymnosperms. Phytotaxa. 2010;19:55–70. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.19.1.3. - DOI
-
- Hao DC, Xiao PG, Huang B, Ge GB, Yang L. Interspecific relationships and origins of Taxaceae and Cephalotaxaceae revealed by partitioned Bayesian analyses of chloroplast and nuclear DNA sequences. Plant Syst. Evol. 2008;276:89–104. doi: 10.1007/s00606-008-0069-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

