Estimating Vocal Fold Contact Pressure from Raw Laryngeal High-Speed Videoendoscopy Using a Hertz Contact Model
- PMID: 34267956
- PMCID: PMC8279006
- DOI: 10.3390/app9112384
Estimating Vocal Fold Contact Pressure from Raw Laryngeal High-Speed Videoendoscopy Using a Hertz Contact Model
Abstract
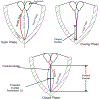
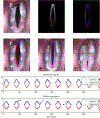
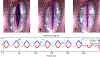
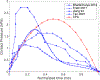
The development of trauma-induced lesions of the vocal folds (VFs) has been linked to a high collision pressure on the VF surface. However, there are no direct methods for the clinical assessment of VF collision, thus limiting the objective assessment of these disorders. In this study, we develop a video processing technique to directly quantify the mechanical impact of the VFs using solely laryngeal kinematic data. The technique is based on an edge tracking framework that estimates the kinematic sequence of each VF edge with a Kalman filter approach and a Hertzian impact model to predict the contact force during the collision. The proposed formulation overcomes several limitations of prior efforts since it uses a more relevant VF contact geometry, it does not require calibrated physical dimensions, it is normalized by the tissue properties, and it applies a correction factor for using a superior view only. The proposed approach is validated against numerical models, silicone vocal fold models, and prior studies. A case study with high-speed videoendoscopy recordings provides initial insights between the sound pressure level and contact pressure. Thus, the proposed method has a high potential in clinical practice and could also be adapted to operate with laryngeal stroboscopic systems.
Keywords: Hertz impact; biomechanical modeling; contact pressure; endoscopy; high-speed video; laryngeal high-speed videoendoscopy; tissue modeling; vocal folds.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Hillman RE; Holmberg EB; Perkell JS; Walsh M; Vaughan C. Objective assessment of vocal hyperfunction: An experimental framework and initial results. J. Speech Hear. Res 1989, 32, 373–392. - PubMed
-
- Karkos P; McCormick M. The etiology of vocal fold nodules in adults. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg 2009,17, 420–423. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
